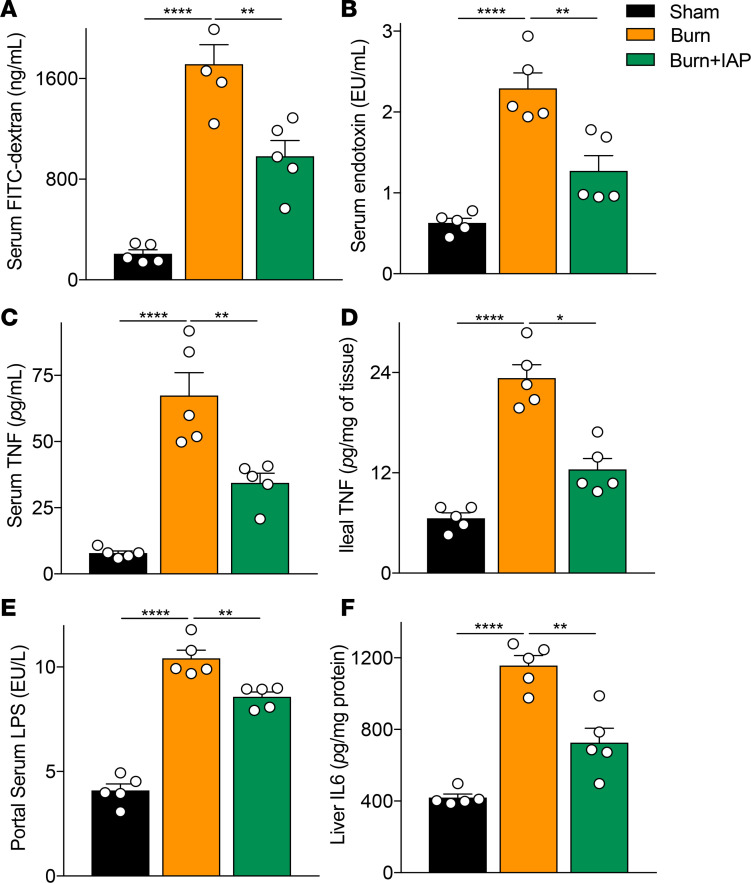
Figure 6. IAP supplementation preserves gut barrier function and attenuates systemic inflammation in a cutaneous burn injury murine model.
(A) Gut permeability at 6 hours after a 30% TBSA dorsal burn insult measured by FITC-dextran levels in the serum 4 hours after intragastric FITC administration. (B) Serum endotoxin levels measured by Limulus amebocyte lysate assay at 6 hours after a 30% TBSA back burn insult. (C) TNF-α levels in the serum measured by ELISA. (D) Ileal inflammation measured by TNF-α levels using ELISA. (E) Portal serum endotoxin levels measured by LAL assay. (F) IL-6 levels in the liver of sham, burn alone mice supplemented with or without IAP measured by ELISA. For multiple comparisons, 1-way ANOVA with multiple post hoc Turkey’s comparisons was performed. Each group included 5 animals and data are representative of 3 biological replicates. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. IAP, intestinal alkaline phosphatase; TBSA, total body surface area.