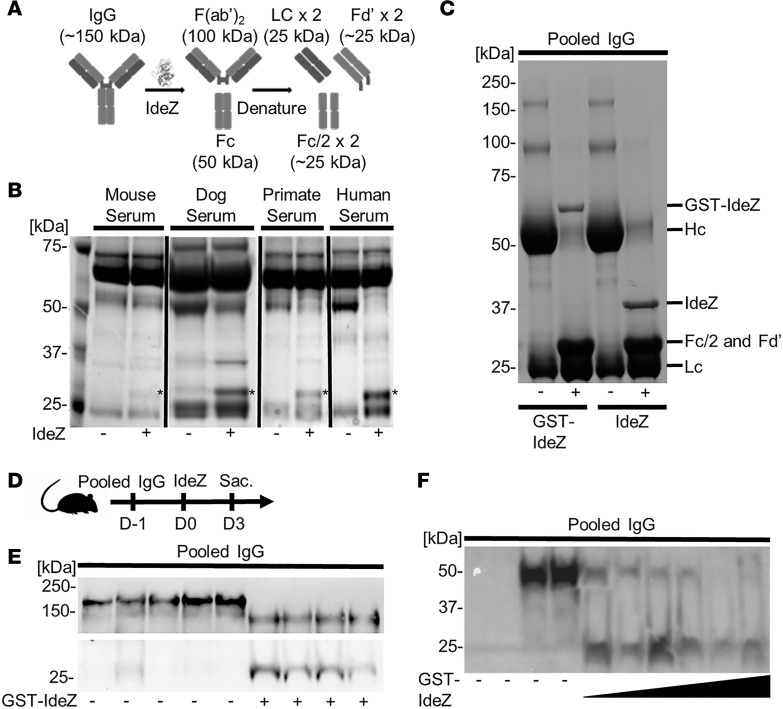
Figure 1. IdeZ cleaves serum antibodies from multiple species.
(A) Schematic outlining IdeZ cleavage of IgG below the hinge region yielding multiple F(ab′)2 and Fc fragments after reduction. (B) Serum samples from mouse, dog, primate, and human untreated (-) or treated (+) with recombinant IdeZ and analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. Gels were then stained with Coomassie blue. * indicates digested Fc/2 and Fd′ fragments. (C) Pooled human IgG untreated (-) or treated (+) with recombinant glutathione-S-transferase–IdeZ (GST-IdeZ) or commercial standard IdeZ and analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. Gels were then stained with Coomassie blue. IgG was cleaved by GST-IdeZ and IdeZ into multiple fragments as indicated. (D) Experimental timeline of in vivo GST-IdeZ dose optimization experiment. Mice were injected with pooled human IgG followed 24 hours later with no injection or injection with 3 different doses of GST-IdeZ. Blood serum samples were collected 72 hours post GST-IdeZ. Sac., sacrifice followed by tissue harvest. (E) Mice were injected IP first with pooled human IgG, followed by IV injection with PBS 24 hours later (-) or recombinant GST-IdeZ (1 mg/kg) (+). Blood samples were taken 72 hours after injection and analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions with immunoblotting. IgG was probed with Fab- and Fc-specific antibodies. (F) Mice were injected IP first with pooled human IgG, followed by IV injection with PBS 24 hours later (-) or recombinant GST-IdeZ at 3 doses (0.25 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, and 2.5 mg/kg) (+). Blood samples were taken 72 hours after injection and analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions with immunoblotting. Human IgG was probed with an Fc-specific antibody. See complete unedited blots in the supplemental material.