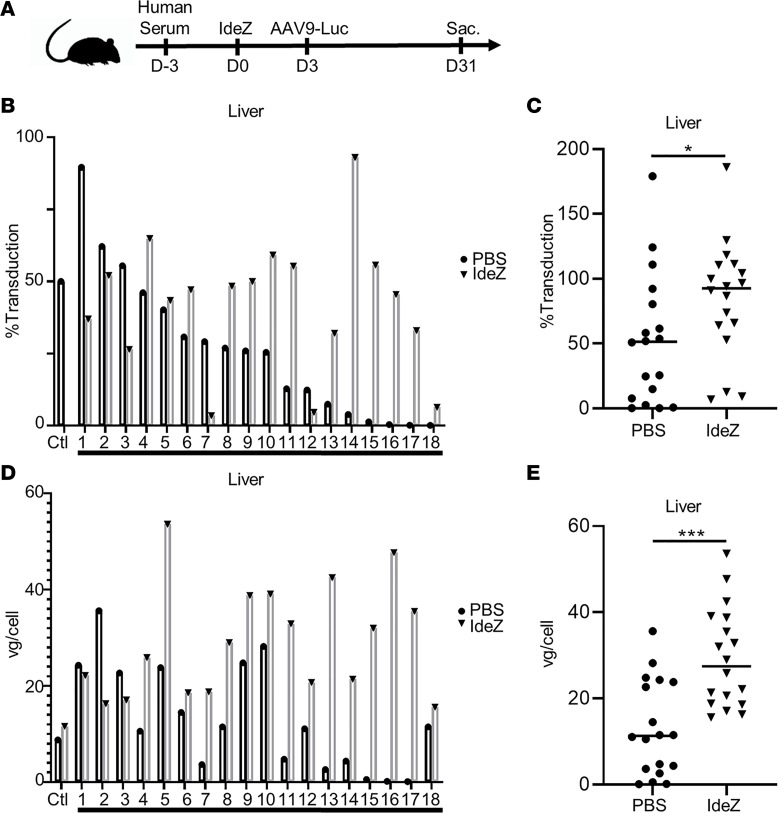
Figure 3. IdeZ rescues AAV9 liver transduction in mice passively immunized with individual human sera.
(A) Schematic demonstrating experimental timeline of human serum, IdeZ, and AAV9-Luc injections. Eighteen human serum samples were tested for their ability to neutralize AAV9 transduction in the liver. Two mice per human serum sample were used for the study, and both mice were injected IP with human serum. Mice were then injected IV 72 hours later with PBS (black bars) or recombinant GST-IdeZ (2.5 mg/kg, gray bars) and subsequently injected IV 72 hours post–IdeZ treatment with AAV9-Luc (1 × 1013 vg/kg). Liver transduction levels were analyzed 4 weeks postinjection. (B) Luciferase transgene expression levels were analyzed 4 weeks postinjection in the livers of passively immunized mice treated with PBS (black bar, black circle) or prophylactically with IdeZ (gray bar, black triangle). Transduction levels were normalized to nonimmunized mice that were injected with AAV9-Luc at the same dose and represented as percentage of control. Each bar represents the average of a technical duplicate from a single animal. (C) Relative liver transduction efficiency of AAV9-Luc in the entire cohort of mice immunized with human sera treated with PBS control (circle) or IdeZ (triangle). Biodistribution of AAV9 vector genomes in the liver for mice passively immunized with individual human serum samples (D) and the entire cohort (E). Vector genome copy numbers per cell were calculated based on normalization to copies of the lamin B2 housekeeping gene. Each bar represents the average of a technical duplicate from a single animal. Significance was determined by the nonparametric Mann-Whitney rank test. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.