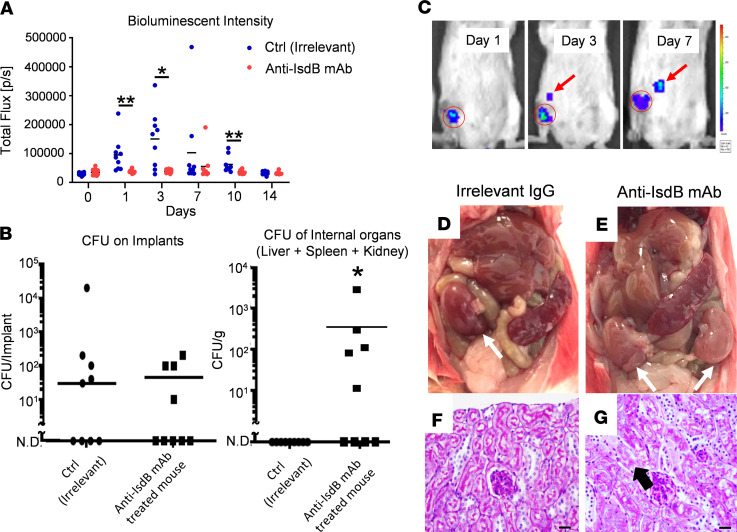
Figure 3. Anti-IsdB mAb passive immunization renders mice susceptible to sepsis following SSI.
(A) Mice were passively immunized with anti-IsdB or irrelevant control mAb (n = 9), challenged with a USA300LAX:Luc-contaminated transtibial implant, and longitudinal BLI was performed as described in Methods. The BLI signal within the tibial ROI for individual mice on the indicated day after challenge is presented with the mean for the group (*P < 0.05 on day 3, **P < 0.01 on days 1 and 10 via exact Wilcoxon test with an adaptive Hochberg multiplicity adjustment). (B) CFUs on the tibial pin and in internal organs were determine on day 14 after infection of passively immunized mice. The incidence and mean level of CFUs on the implants in both groups were similar (lower limit of detection <10). However, CFUs in internal organs of control mAb-treated mice were not detected (N.D.), while anti-IsdB mAb–treated mice displayed evidence of MRSA dissemination (n = 9, *P < 0.05 via Fisher’s exact test, lower limit of detection <10). (C) Longitudinal BLI images with heatmap signal intensities of a representative mouse passively immunized with IsdB with evidence of MRSA dissemination from the surgical site (red circled region) to internal organs (red arrow). (D–G) Gross anatomy and renal histology of internal organs from mice passively immunized with control IgG and anti-IsdB mAb, illustrating the normal versus pale kidneys (white arrows) and evidence of renal tubular necrosis (black arrow) in anti-IsdB–treated mice. Scale bar: 20 μm.