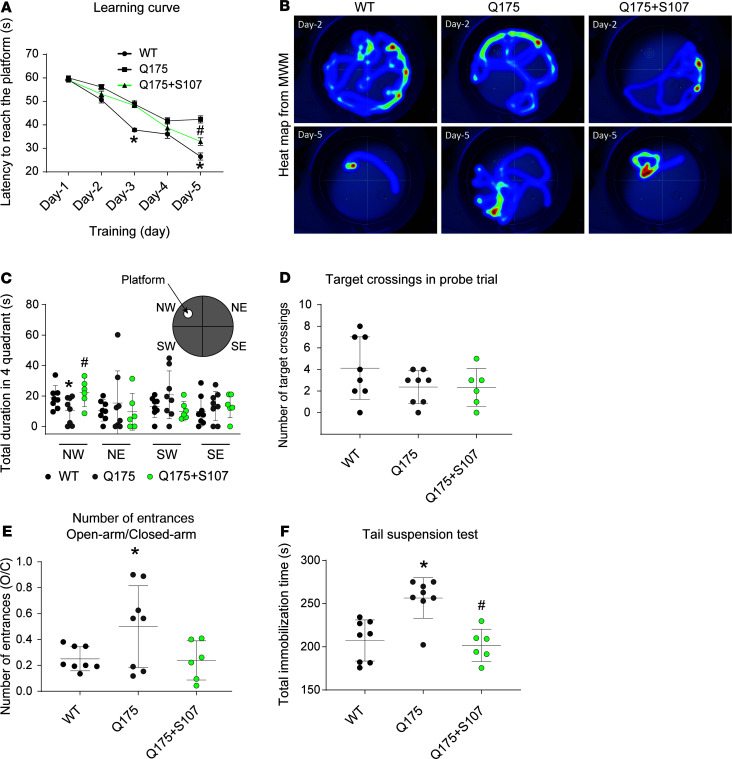
Figure 3. Long-term learning and memory deficits in Q175 mice.
S107 treatment targeting RyR2 channels improves cognitive function in HD. (A) Learning curves showing the escape latency during a 5-day training period in the Morris water maze (MWM). (B) The heatmaps from all the training trials were recorded (Noldus Information Technology Inc.) and downloaded. Representative heatmaps from WT (left column), Q175 (middle column), and S107-treated Q175 (right column) on day 2 (upper panels) and day 5 (lower panels) are shown. (C) The time spent in all quadrants. (D) The number of target crossings on day 6 probe trial of the MWM. (E) The ratio of the number of entries to open arms versus closed arms of the elevated plus maze (EPM). (F) Total immobilization time of mice during 300 seconds of tail suspension test. The same groups of mice were used for MWM, EPM, and tail suspension. WT (n = 8), Q175 (n = 8), and Q175+S107 (n = 6). Data (mean ± SD) analysis was performed by 1-way ANOVA. Bonferroni’s posttest revealed *P < 0.05 vs. WT, #P < 0.05 vs. Q175.