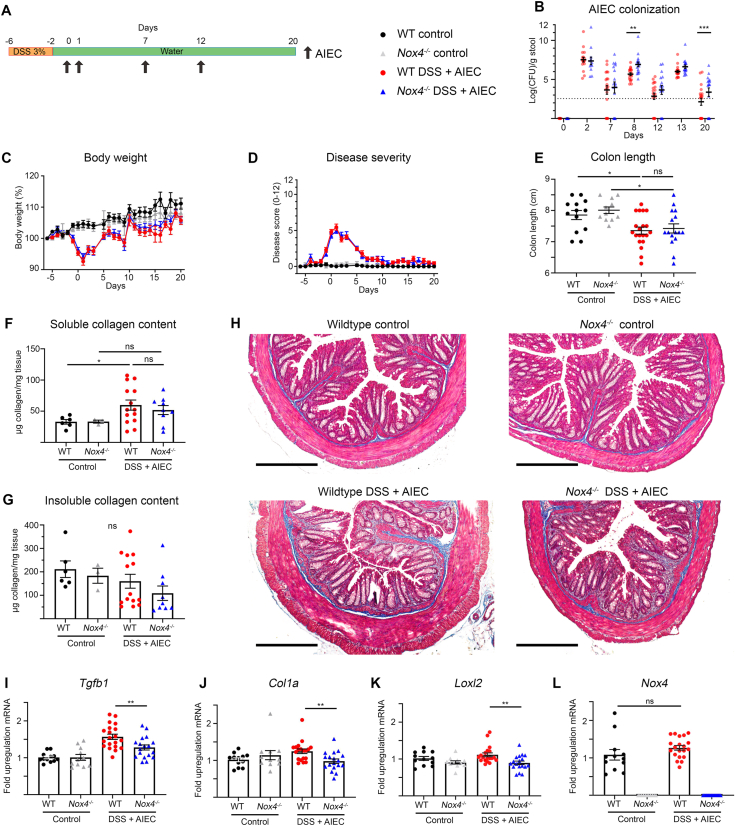
Fig. 4.
AIEC-induced intestinal fibrosis is not attenuated in Nox4−/−mice. Mice were exposed for 4d to 3% DSS (or water) before repeated oral administration of AIEC (1 × 109 CFU, arrow) (or PBS as control) (A). (B) Quantification of AIEC in feces of Nox4−/− mice compared to wildtype mice; dotted line represents detection limit. (C) Body weight loss and (D) disease severity scoring. Colon inflammation and fibrosis at d20 was assessed by (E) colon length, (F, G) soluble and insoluble collagen, and (H) Masson trichrome stained sections with collagen in blue; scale bar 300 μm, and qPCR on colonic mRNA, normalized to wildtype mice, of (I) Tgfb1, (J) Col1a, (K) Loxl2, and (L) Nox4. (B, C, E-G, I-L) represented as mean ± SEM, (D) represented as median ± IQR, (B) data were log-transformed then analyzed with multiple unpaired t tests with Holm-Sidak correction, (E-G) data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test, (I, J, K) by unpaired t-test between wildtype and Nox4−/− treated groups, or (L) Welch's t-test between wildtype groups. Data represent three independent experiments.