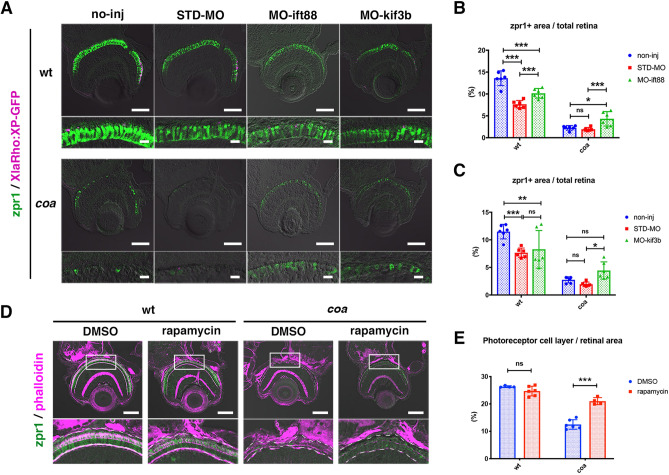
Figure 6.
Blockade of intracellular vesicular transport rescues photoreceptor apoptosis in coa mutants. (A) Retinas of 3.5 dpf wild-type and coa mutant embryos injected with standard MO, MO-ift88, or MO-kif3b. Cone photoreceptors and rod OSs were visualized by labeling with zpr1 antibody (green) and fluorescent signals from Tg[XlaRho:XP-GFP] (magenta). In coa mutant retinas injected with either MO-ift88 or MO-kif3b, cone photoreceptor degeneration was partially inhibited. Scale: 50 μm (upper) and 10 μm (lower). (B) Percentage of zpr1-positive area relative to total retinal area in wild-type and coa mutant embryos injected with standard MO and MO-ift88. MO-itf88 significantly rescued photoreceptor apoptosis in coa mutants. Means ± SD. Two-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.005. (C) Percentage of zpr1-positive area relative to total retinal area in wild-type and coa mutant embryos injected with standard MO and MO-kif3b. MO-kib3b significantly rescued photoreceptor apoptosis in coa mutants. Means ± SD. Two-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005. (D) Retinas of 3.5 dpf wild-type and coa mutant embryos treated with DMSO or rapamycin. Lower panels indicate higher magnification of squares in upper panels. The outline of the photoreceptor cell layer (white dotted lines) was visualized by labeling with zpr1 (green) and phalloidin (magenta). In coa mutant retinas treated with rapamycin, the size of photoreceptor cell layer increased. Scale: 50 μm. (E) Percentage of the photoreceptor cell layer relative to total retinal area in wild-type and coa mutant embryos treated with DMSO and rapamycin. Rapamycin treatment significantly recovers the size of photoreceptor cell layer in coa mutants. Means ± SD. Two-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test. ***p < 0.005.