Figure 6.
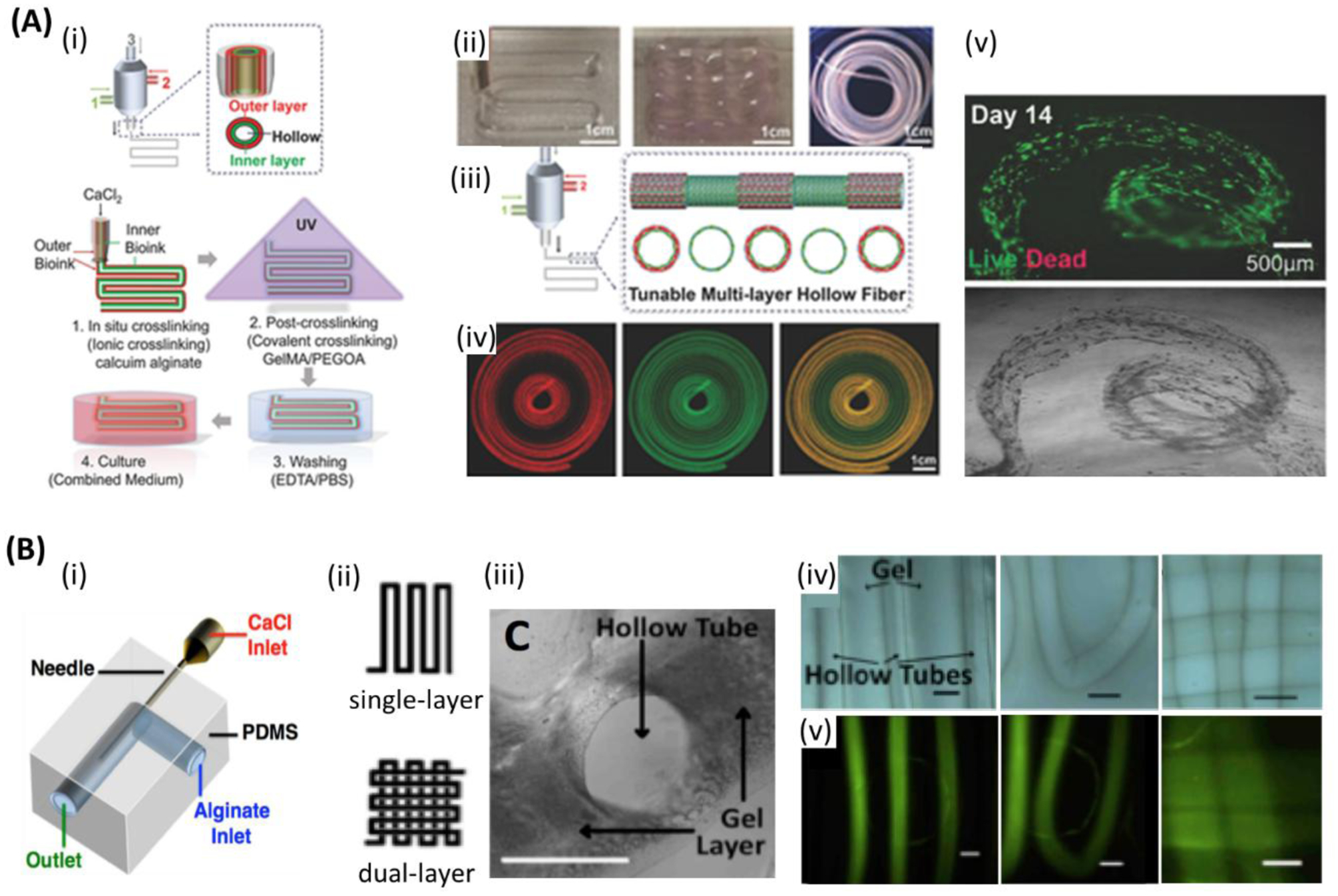
Microfluidic bioprinting of vascularized tissue. A) (i) Steps followed for microfluidic bioprinting of multilayered tubular hydrogel constructs. (ii) Images of bioprinted tubular constructs. (iii) Fabrication of tunable single and double layered tubes. (iv) Fluorescence images representing dynamic variation between single and double layered tube. (v) Live/dead assay of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and human smooth muscle cells (hSMCs) encapsulated within the tubes on day 14. Scale bars: (ii, iv) 1cm, (v) 500 μm. Reproduced with permission.[85] Copyright 2018, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. B) Co-axial microfluidic nozzle for hollow Ca-alginate filaments formation. (ii-v)) Continues gel layer with embedded single and dual layer channels. (ii) Single and dual layer patterns. (iii) Cross-section of the continues gel with embedded hollow channels. (iv) Printed parallel straight channels (left), their arc connections (middle), and dual layer channels (right). (v) Fluorescent images illustrating the nanoparticles flow along the channels shown in (iv), respectively. Scale bars: 1 mm. Reproduced with permission.[187] Copyright 2016, SPIE.
