Fig. 5. Ca2+-binding site of MC4R and comparison with other known GPCR cation-binding sites.
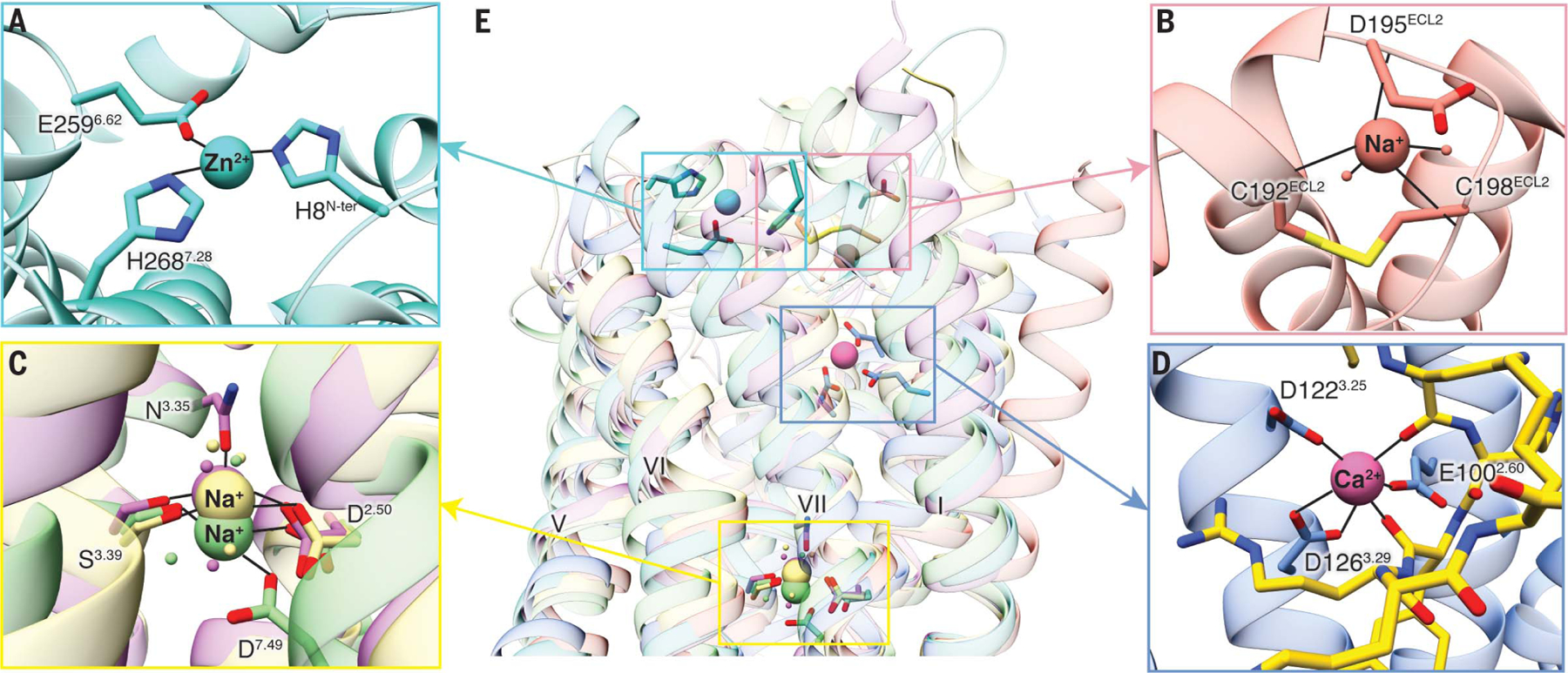
(A) Zn2+ ion-binding site is located at the extracellular side of PAFR (PDB ID 5ZKQ, turquoise). Residues are shown in turquoise. (B) Extracellular binding site of Na+ on β1AR (PDB ID 4BVN, salmon) is located at the extracellular loops. (C) Conserved Na+-binding site in most class A GPCRs including D2.50 and S3.39 (A2AAR, PDB ID 4EIY, khaki). Both proteinase-activated receptor 1 (PAR1, PDB ID 3VW7, light green) and d-type opioid receptor (DOR, PDB ID 4N6H, orchid) have an additional interaction residue, D7.49 and N3.35, respectively. (D) Binding site for Ca2+ in the MC4R is surrounded by residues from helices II and III and by carbonyl oxygens from the ligand, near the extracellular face. Ca2+ is shown as a pink sphere. The peptide ligand is represented as gold sticks. (E) Superposition of MC4R, PAFR, β1AR, A2AAR, PAR1, and DOR shows the comparison of known cation-binding sites. All coordinate bonds are shown in solid black lines.
