Figure 1.
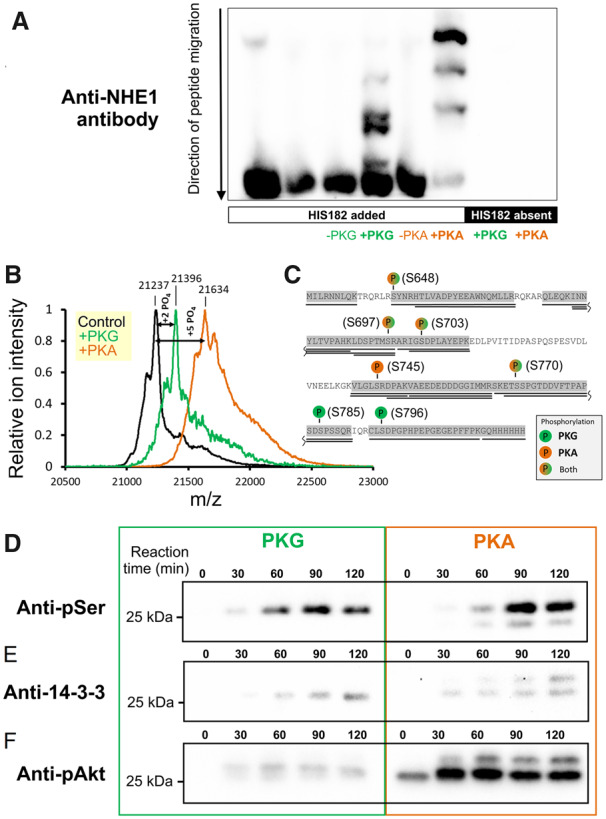
Phosphorylation of the NHE1 C-terminus by PKA and PKG. (A) Various combinations of kinase (PKA or PKG; 8 ng/µL) and protein (His182; 20 ng/µL) were reacted in vitro and run on a Phos-tag gel to seek evidence for differences in phosphorylation pattern. (B) His182 (100 ng/µL) was reacted in vitro with PKA (100 ng/µL) or PKG (50 ng/µL) and analysed by LC-MS/MS mass spectrometry for phosphorylation sites. Results indicated a mean phosphorylation stoichiometry of five and two phosphate groups introduced by PKA and PKG, respectively. (C) Residues identified as being phosphorylated by PKA and PKG. (D) Time course of reaction between His182 (20 ng/µL; plus 500 µM ATP) and either PKG (8 ng/µL; left) or PKA (8 ng/µL; right). Western blots were performed using an antibody raised against phosphorylated serine residues. (E) Western blot performed using antibody against the phosphorylated 14-3-3 binding motif (detecting Ser703 in NHE1). (F) Western blot performed using antibody against phosphorylated Akt substrate (Ser648 in NHE1). Note: blots for PKA- and PKG-reacted His182 were prepared with the same amount of substrate and developed simultaneously with identical exposure time. See Supplementary material online, Figure S1 for loading controls.
