Figure 3. Immunocompetent OOC models.
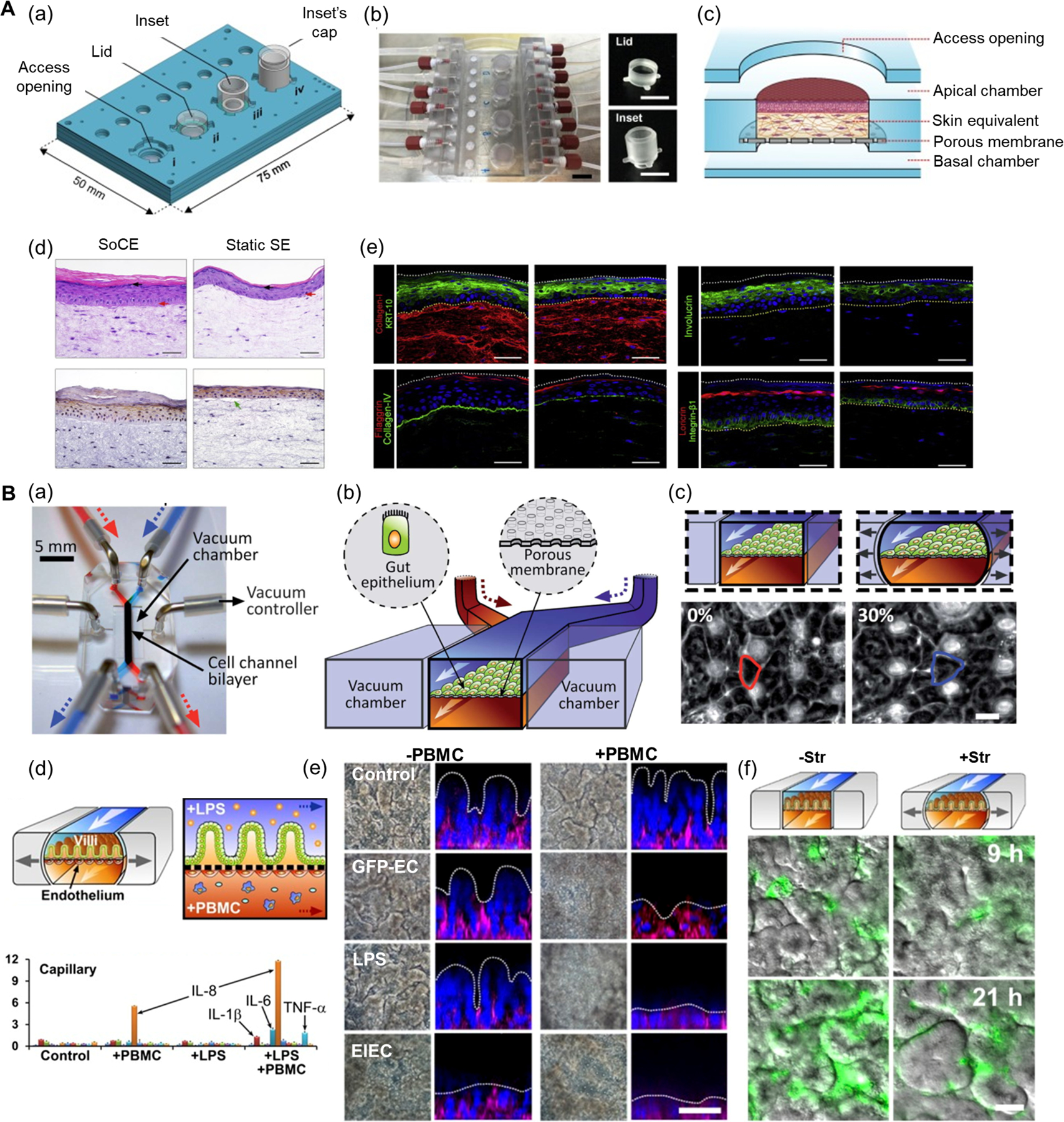
A) Skin-on-a-chip model. (a) Schematics of the four-chamber skin-on-a-chip device with each unit having different operational configurations. (b) Photographs of the skin-on-a-chip device with interchangeable lid and inset. (c) Schematics of the skin-on-a-chip for human fibroblasts and keratinocytes coculture. (d) Histological images of the epidermal layer from skin-on-a-chip compared to skin equivalents grown in static culture inserts. (e) Fluorescent images showing the expressions of keratinocyte differentiation markers KRT-10 (green), filaggrin (red), involucrin (green), and loricrin (red); constituents of basement membrane zone collagen type IV (green), integrin-β1 (green), and dermal matrix protein collagen type I (red). Reproduced under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0.[103] International Public License for open access articles. B) Human gut-on-a-chip. (a) Photograph of the gut-on-a-chip device. (b) Schematics of the gut-on-a-chip device with epithelial cell layer grown on the porous membrane and vacuum chambers on the sides. (c) Schematics (top) and phase-contrast images (bottom) of the intestinal monolayer within the gut-on-a-chip with or without mechanical strain (30%). Reproduced with permission.[124] Copyright 2012, Royal Society of Chemistry. (d) The schematics showing the interface between the intestinal villus epithelium and vascular endothelium (top) and secretions of proinflammatory cytokines after costimulation with LPS and PBMCs (bottom). (e) Phase-contrast images and fluorescence confocal micrographs of intestinal villus damage in response to GFP-EC, LPS, and EIEC in the absence or the presence of PBMCs. (f) Overlaid fluorescence and DIC microscopic views showing growth of GFP-EC on the intestinal villi in the absence (-Str) or presence (+Str) of cyclic stretching motions (10% in cell strain, 0.15 Hz in frequency) for 9 h and 21 h. Reproduced under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0.[125] International Public License for open access articles. DIC: differential interference contrast, EIEC: enteroinvasive Escherichia coli, GFP-EC: GFP-labeled Escherichia coli, LPS: lipopolysaccharides, Str: cyclic stretching motion.
