Figure 5. Immunotherapy-on-a-chip models.
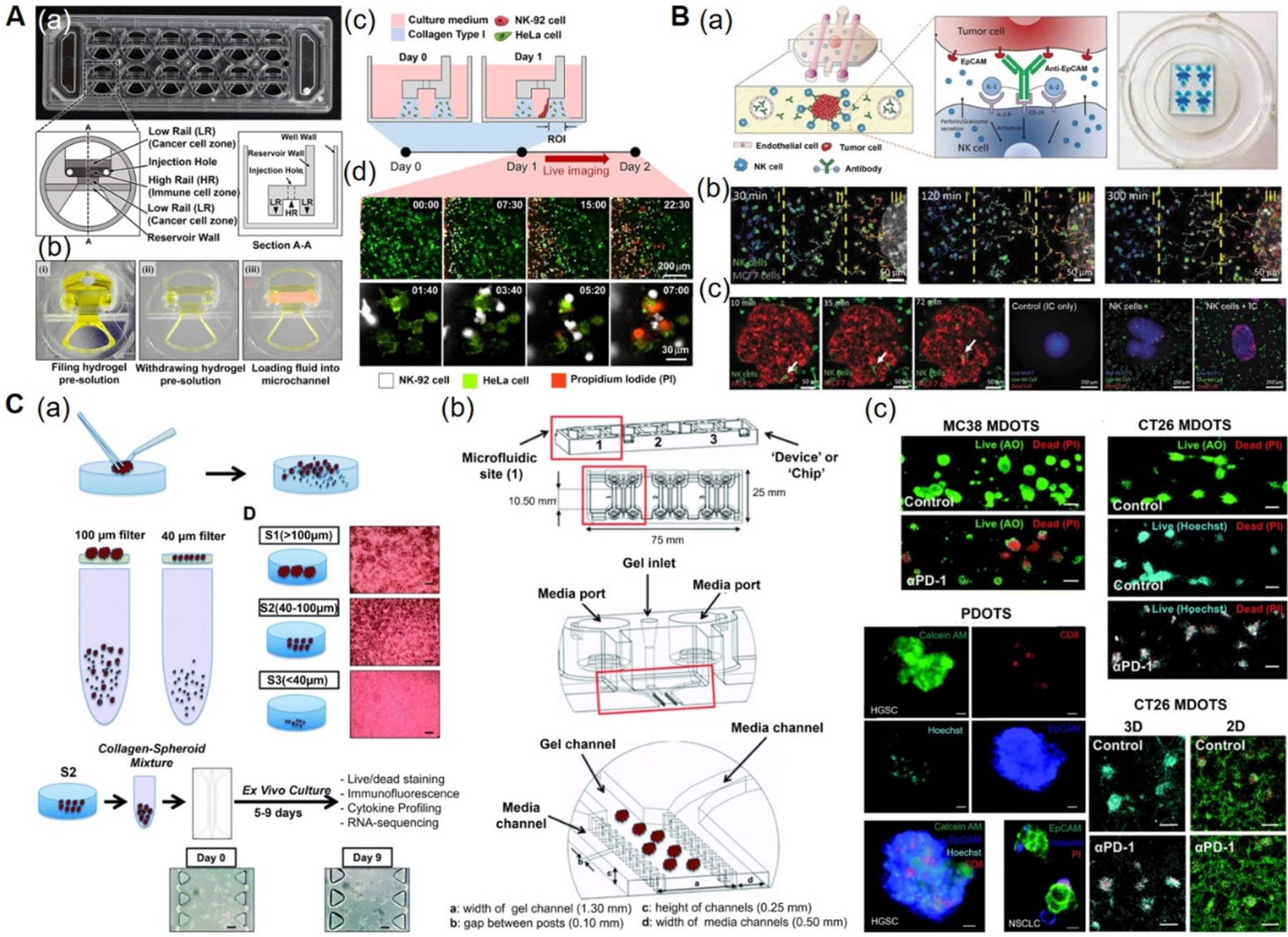
A) CACI-IMPACT platform for 3D cytotoxicity assay. (a) Photograph and schematics of microfluidic device consisting of rail-based microstructures integrated in a 2 × 6 rectangular array of wells. (b) Photographs showing the compartments within the device. Each well consists of two LRs for hydrogel patterning and one HR forming a channel for fluid flow after hydrogel crosslinking. (c) Schematics showing the loading of HeLa cells embedded in collagen into LRs at Day 0 and NK-92 cells into a microchannel after 24 h. The device was tilted to 90° for 20 min to accumulate NK-92 cells on one side of the collagen gel. (d) Time-lapse images showing the migration of NK-92 cells towards the collagen matrix containing HeLa cells. Time is indicated in hour:minute in the top right corner of each image. Reproduced under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0.[162] International Public License for open access articles. B) Microfluidic device to study ADCC in NK cells. (a) Schematics (left) and photographs (right) of the device consisting of central chamber with a tumor spheroid in collagen hydrogel and two flanking lateral lumens with endothelial cells mimicking blood vessels. NK cells and/or antibodies were embedded in the hydrogel or perfused through the lateral lumens. (b) Time-lapse images showing directional migration of NK-92 cells (labeled in green) towards MCF7 spheroid (labeled in red). The field of view was divided in three regions: distal (I), central (II), and proximal (III) to analyze NK cell migration. (c) Time-lapse images showing the migration of NK-92 cells within the tumor sphere using an ameboid movement (white arrow), followed by the images showing the anti-EpCAM immunocytokine, IC65-induced cell cytotoxicity, when used in combination with NK-92.CD16V cells. Reproduced with permission.[45,163] Copyright 2018, Taylor & Francis. C) 3D microfluidic device for MDOTS/PDOTS culture. (a) Schematics showing the preparation and culture of MDOTS/PDOTS (S2 fraction) from murine or patient-derived tumor specimens. (b) Schematics showing the different components of the microfluidic device. Each device comprised of center gel region and side media channels separated by posts, gel loading port and media ports. (c) Fluorescence images showing the live/dead analysis of MDOTS in the presence of anti-PD-1 antibody or isotype control IgG, in 3D microfluidic and 2D cultures. Reproduced under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0[166] Unported Licence for open access articles. ADCC: antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity, AO: acridine orange, CACI-IMPACT: cytotoxicity assay for cancer immunotherapy-injection molded plastic array culture platform, 2D: two-dimensional, 3D: three-dimensional, EpCAM: epithelial cell adhesion molecule, HR: high rail, IC: immunocytokine, IgG: immunoglobulin G, LR: low rail, MDOTS: murine-derived multicellular organotypic tumor spheroids, NK: natural killer, PDOTS: patient-derived multicellular organotypic tumor spheroids, PD-1:programmed cell death protein 1, PI: propidium iodide.
