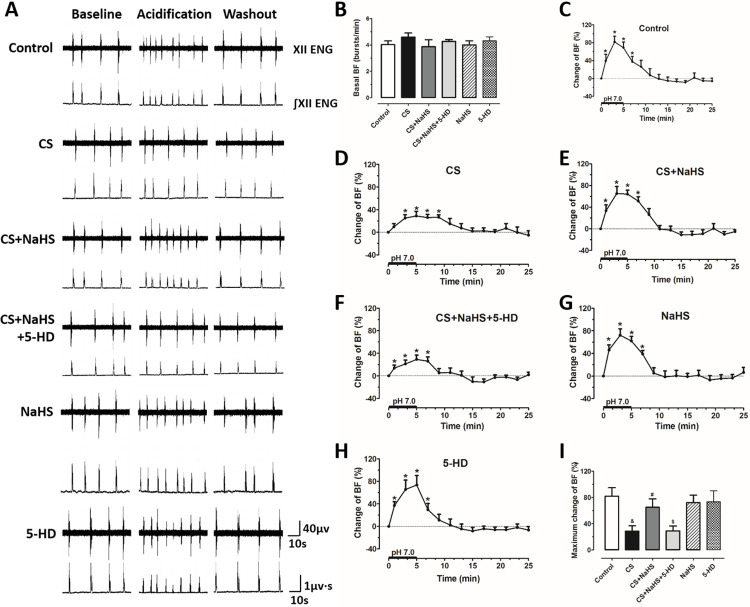
Fig 1. MitoKATP channel blocker restrains the protective effect of NaHS on maternal CS exposure-induced impairment of central chemoreception in offspring medullary slices.
(A) Typical recordings of hypoglossal rootlets discharges in medullary slices of the offspring. In each panel, the upper and lower lines indicate the raw (XII ENG) and integrated (∫XII ENG) activities of hypoglossal rootlets during baseline, acidification and washout, respectively; (B) comparison of basal burst frequency (BF) in different groups. Changes of BF in the (C) Control group (n = 8), (D) CS group (n = 8), (E) CS+NaHS group (n = 8), (F) CS+NaHS+5-HD group (n = 6), (G) NaHS group (n = 8) and (H) 5-HD group (n = 6); (I) comparison of maximum changes of BF of hypoglossal rootlets discharges responding to acidified perfusion among all groups. XII ENG: electroneurogram of hypoglossal rootlets, ∫XII ENG: integrated XII ENG. *P<0.05 vs. 0 min; &P<0.05 vs. Control group; #P<0.05 vs. CS group; $P<0.05 vs. CS+NaHS group.