Figure 1.
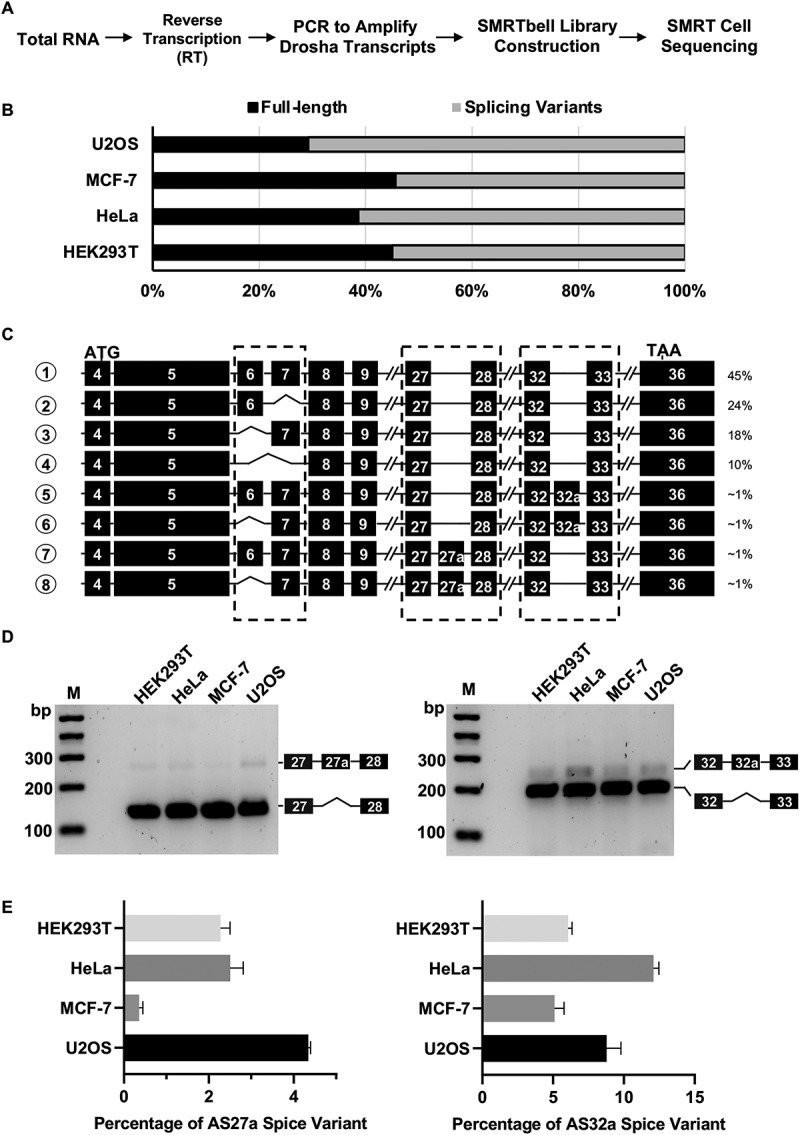
Identification of Drosha splice variants in human cells.
(A) Schematic representation of library construction procedures for PacBio sequencing. (B) Quantitation of Drosha full length (FL) transcripts and splice variants based on PacBio sequencing results in four human cell lines. (C) Schematic diagram of most abundant Drosha transcripts in HEK293T cells. ATG and TAA indicated positions of translation start codon and stop codon in exons, respectively. Dashed-line box indicates where major splicing events were identified in the coding regions. (D) Validation of Drosha alternative splice variants by RT-PCR. Drosha cDNAs were amplified with primers spanning exon27-exon28 and exon32-exon33, respectively. PCR products were confirmed with Sanger sequencing and are labelled correspondingly in the agarose gel image. (E) Quantification of Drosha isoforms in human cells. The amount of each isoform in HEK293T, HeLa, MCF-7, and U2OS cells was measured by real-time qPCR with isoform-specific primers (See methods for more details). The corresponding standard curves can be found in Supplementary Fig. S3.
