Figure 4.
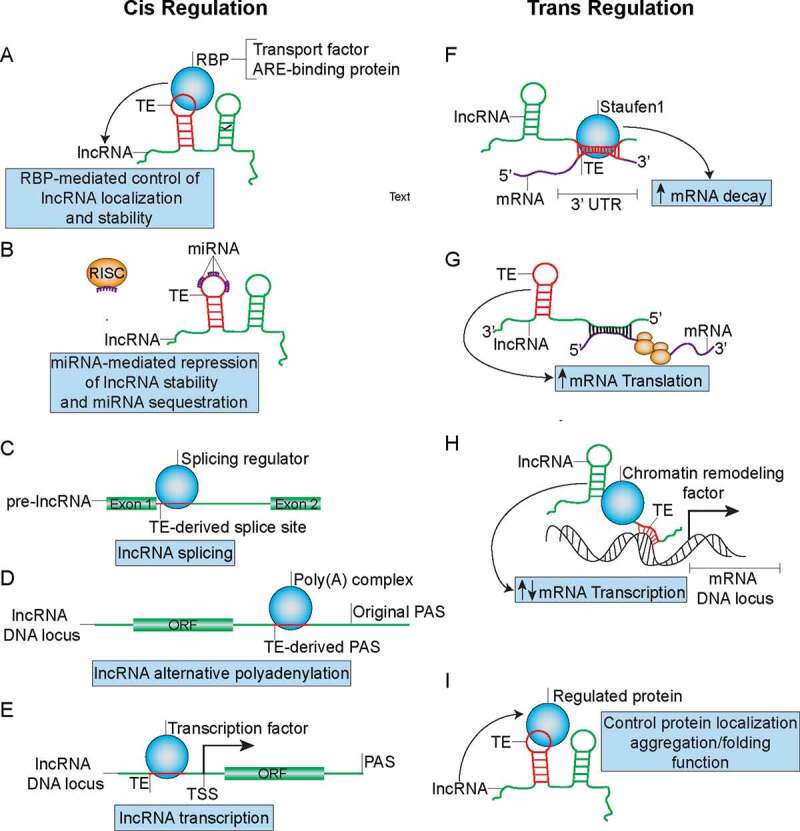
TE-mediated regulation of lncRNA metabolism and function in both cis and trans manners that can influence cancer development. (A) TEs can modulate lncRNA localization and stability by functioning as binding sites for RBP complexes. (B) TEs can function as miRNA binding sites on lncRNAs to control lncRNA stability and may sequester miRNAs from their active binding sites on other transcripts. (C) TEs may function as splice-sites that can be recognized by splicing regulators such as HNRNPC to regulate maturation of pre-lncRNAs. (D) TEs can from PAS to promote APA and formation of short lncRNA transcripts. (E) TEs promote formation of transcription factor binding sites to regulate lncRNA transcription. (F) TEs mediate lncRNA binding to mRNA through partial complementary base pairing in order to promote SMD. (G) TEs mediate antisense lncRNA’s ability to promote translation of sense mRNA. (H) TEs can also mediate lncRNA’s recruitment of chromatin remodelling factors to promoter regions of certain gene loci through formation of dsDNA-RNA triplexes in order to regulate mRNA transcription. (I) TEs embedded in lncRNA can direct RBP localization, aggregation/folding and function.
