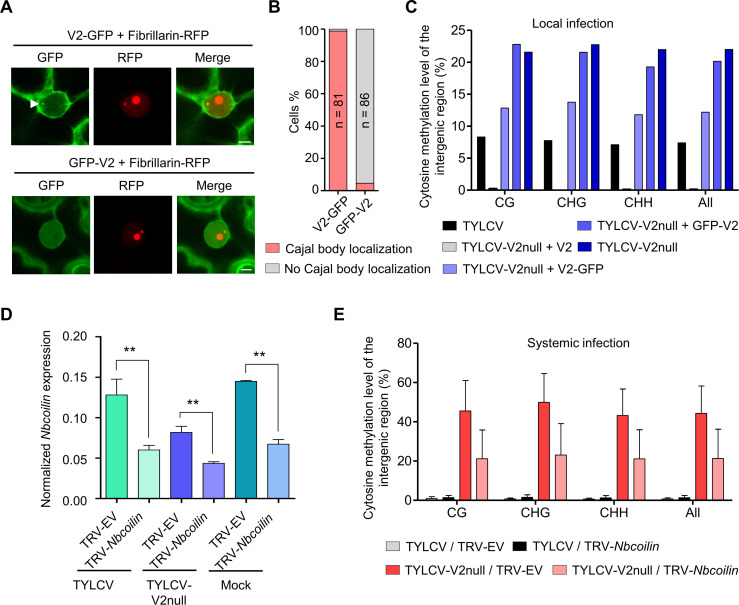
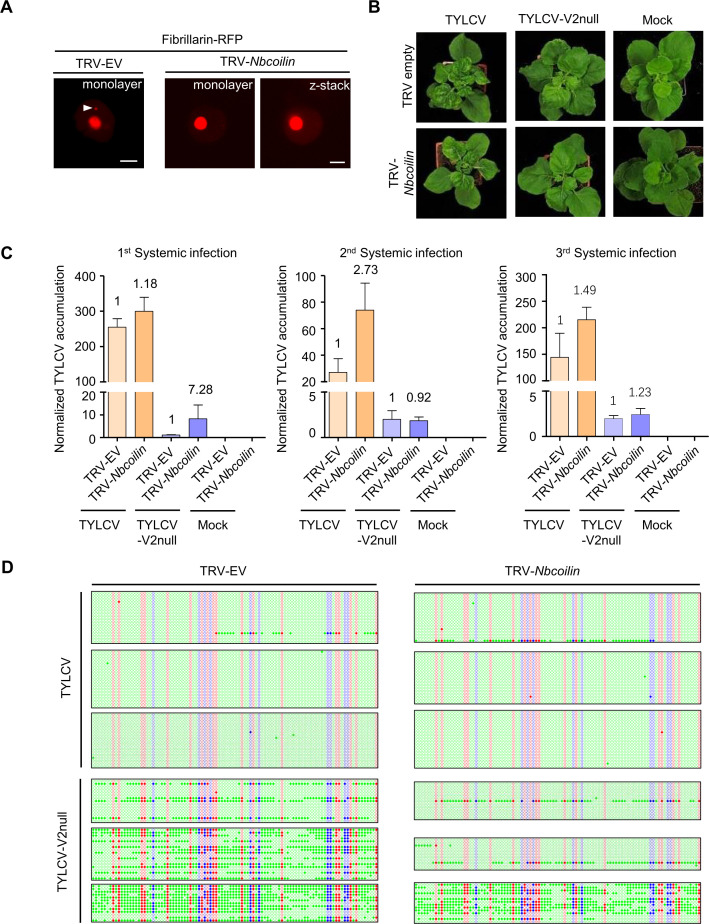
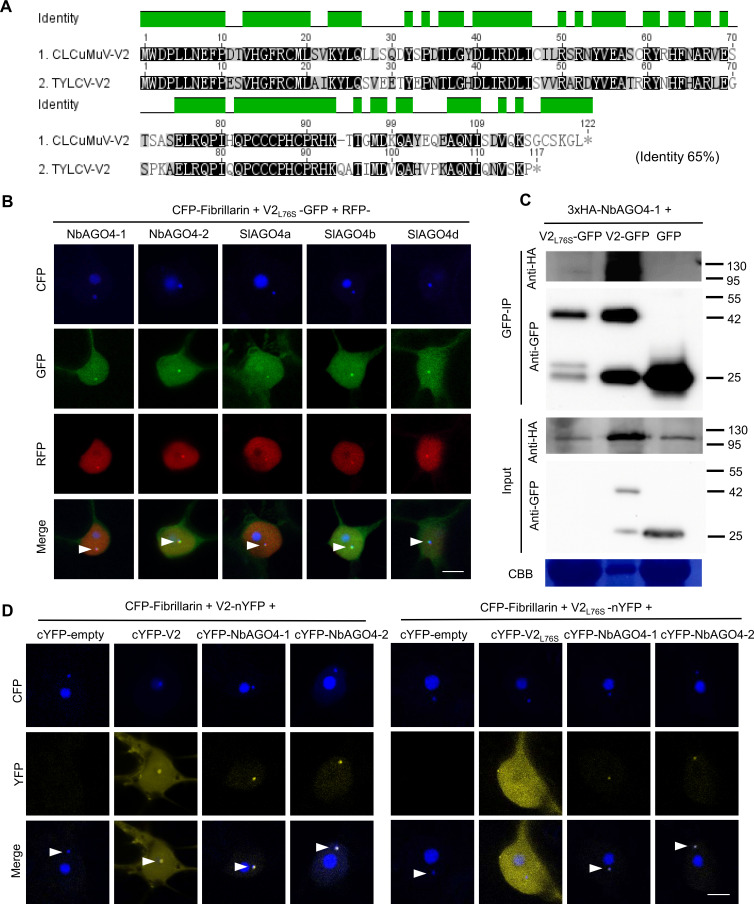
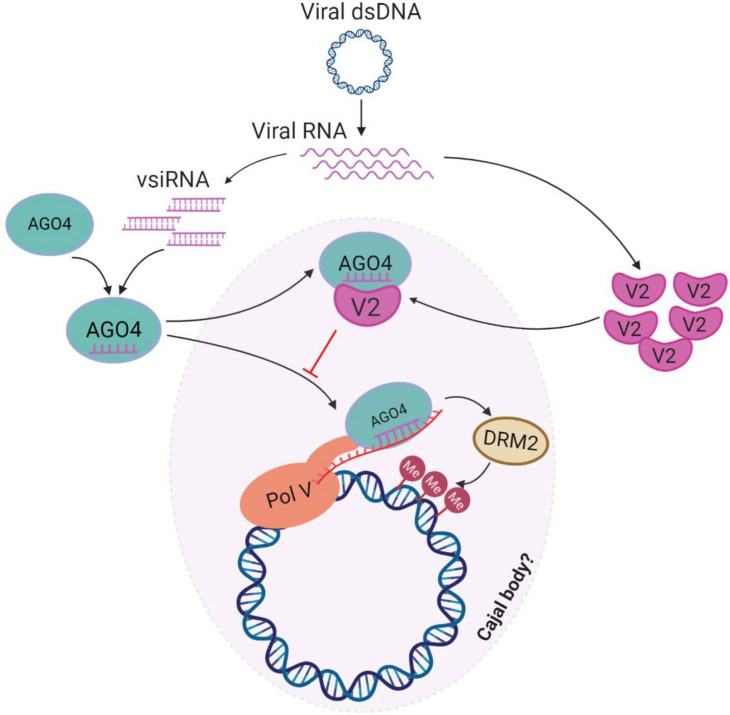
Figure 7. Methylation of the viral DNA and its suppression by V2 occur in a Cajal body-dependent manner.
(A) V2-GFP co-localizes with Fibrillarin-RFP (nucleolus and Cajal body marker) in the Cajal body, while GFP-V2 does not. RFP-Fibrillarin and V2-GFP or GFP-V2 were transiently co-expressed in N. benthamiana epidermal cells. Confocal images were taken at two days after infiltration. Arrowheads indicate the position of the Cajal body. Bar, 5 μm. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (B) Quantification of Cajal body localization of V2-GFP or GFP-V2. (C) V2-GFP, but not GFP-V2, can restore the suppression of viral DNA methylation of a V2 null TYLCV mutant in local infection assays. Cytosine methylation in the intergenic region (IR) of the V2 null mutant genome in locally infected leaf patches of N. benthamiana expressing V2, V2-GFP, or GFP-V2 was detected by bisulfite sequencing at 3 days post-inoculation (dpi). TYLCV or TYLCV-V2null alone were used as controls. The original single-base resolution bisulfite sequencing data are shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 1B. This experiment was repeated twice with similar results. (D) Nbcoilin expression in Nbcoilin-silenced (TRV-Nbcoilin) and control plants (TRV-EV) infected with TYLCV, TYLCV-V2null, or mock-inoculated at 3 wpi measured by RT-qPCR. Gene expression was normalized to NbTubulin. Values are the mean of six independent biological replicates; error bars indicate SEM. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference according to Student’s t-test. **: p<0.01. (E) Percentage of methylated cytosines in the intergenic region (IR) of TYLCV in systemic infection assays with TYLCV wild-type or V2 null mutant (TYLCV-V2null) in Nbcoilin-silenced (TRV-Nbcoilin) or control (TRV-EV) N. benthamiana plants at 3 weeks post-inoculation (wpi), as detected by bisulfite sequencing. Values are the mean of three independent biological replicates; error bars indicate SEM. The original single-base resolution bisulfite sequencing data are shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 2D.