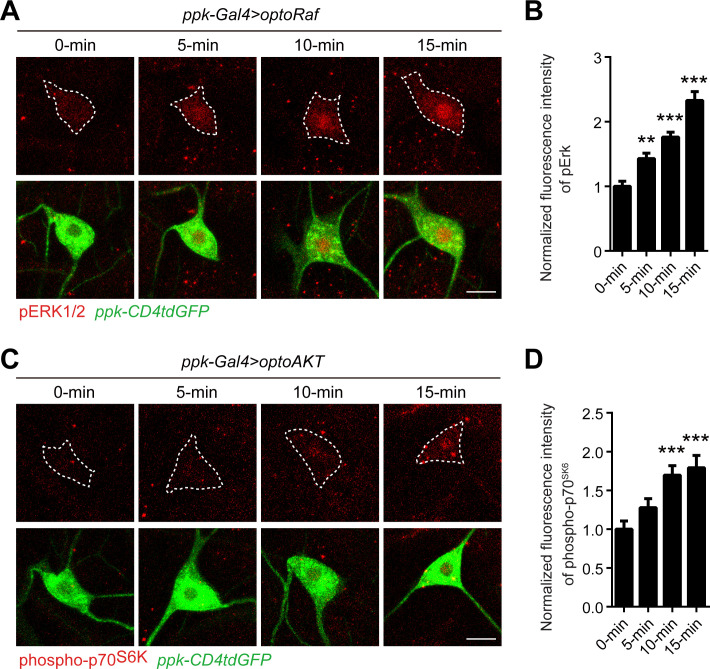
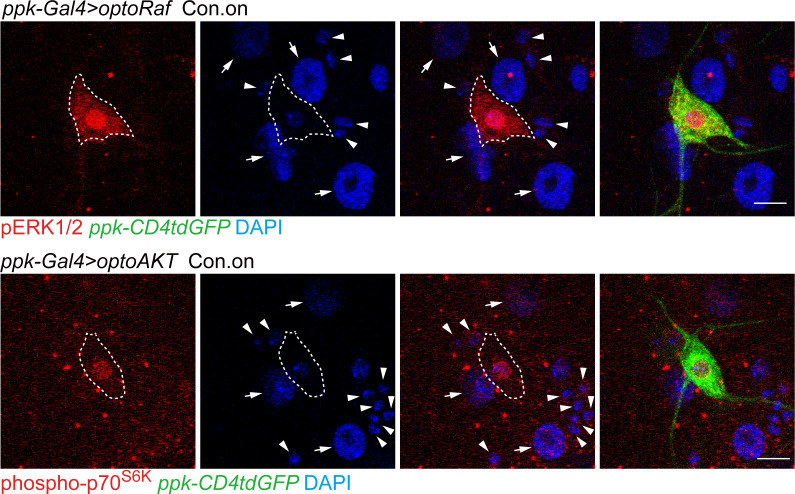
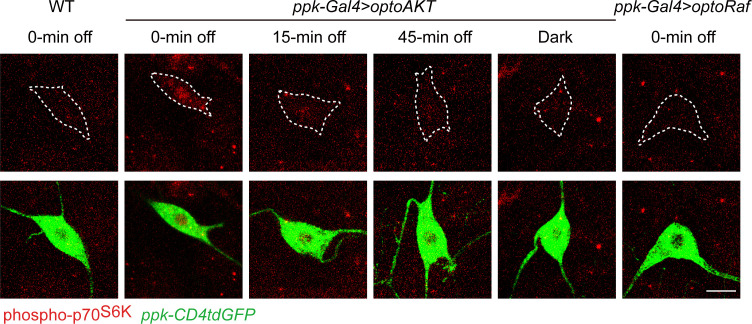
Figure 2. Activation of optoRaf but not optoAKT increases C4da neuron dendrite complexity.
(A–D) 15 min blue light stimulation activates optoRaf and optoAKT in flies in vivo. After the light was off, the downstream effectors inactivated gradually. (A) The body walls from WT and optoRaf expressing larvae were dissected and stained for pERK1/2. The 15 min continuous light illumination leads to the enhanced fluorescent intensity and nuclear translocation of pERK in the optoRaf-expressing C4da neurons (labeled by ppk-CD4tdGFP). pERK signal is significantly increased even at 45 min after the light was off. Notably, the ERK signaling is not activated by light stimulation in optoAKT-expressing neurons. C4da neuron cell bodies are outlined by dashed white lines. Scale Bar = 10 μm. (B) Phospho-p70S6K is activated by light illumination in optoAKT expressing neurons, and gradually returned to baseline after blue light was shut off. (C) Qualification of pERK fluorescence intensity in (A). The intensity of pERK in transgenic larvae was normalized to that of WT. WT (0 min off) N = 19, optoRaf (0 min off) N = 16, optoRaf (15 min off) N = 19, optoRaf (45 min off) N = 18, optoRaf (dark) N = 18, optoAKT (0 min off) N = 19 neurons. (D) Qualification of phospho-p70S6K fluorescence intensity in (B). The intensity of phospho-p70S6K in transgenic larvae was normalized to that of WT. WT (0 min off) N = 18, optoAKT (0 min off) N = 19, optoAKT (15 min off) N = 23, optoAKT (45 min off) N = 20, optoAKT (dark) N = 16, optoRaf (0 min off) N = 23 neurons. (E–G) Activation of Raf/MEK/ERK but not AKT signaling by 72 hr' light stimulation increases dendrite outgrowth and branching in C4da neurons. (E) Representative images of C4da neurons from WT, optoRaf and optoAKT expressing larvae with 72 hr' light stimulation and the unstimulated controls. Neurons were reconstructed with Neuronstudio. Scale bar = 50 μm. (F) Quantification of total dendrite length of C4da neurons. (G) Qualification of dendritic branch number. WT (light) N = 21, optoRaf (light) N = 21, optoRaf (dark) N = 21, optoAKT (light) N = 20, optoAKT (dark) N = 20 neurons. All data are mean ± SEM. The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. See also Figure 3—figure supplements 1–2.