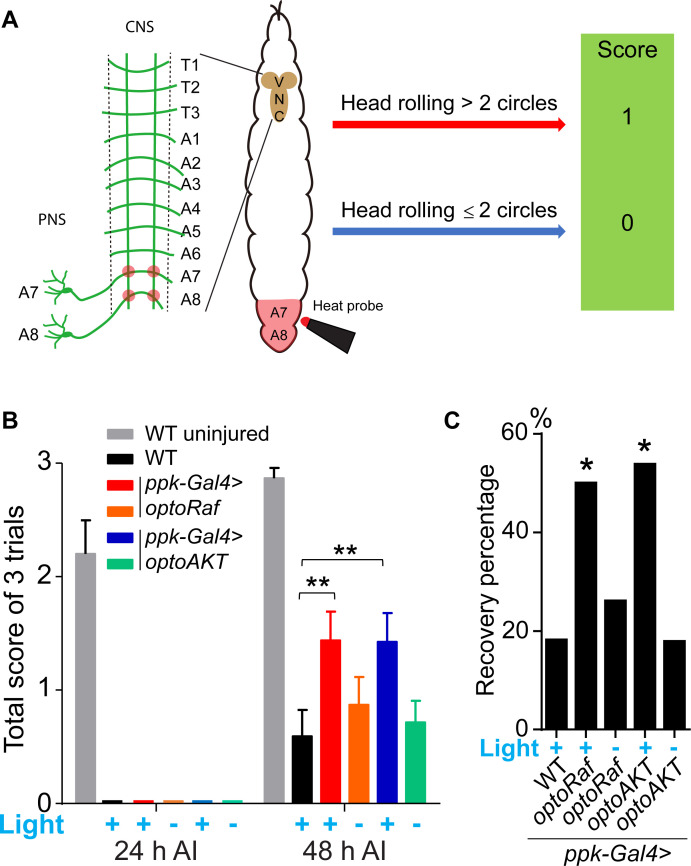
Figure 6. Activation of optoRaf or optoAKT promotes functional regeneration after CNS injury.
(A) A schematic drawing of the behavioral recovery test. The A7 and A8 C4da neuron axon bundles (corresponding to the A7 and A8 body segments) in the VNC were injured by laser and the larva was then subjected to three consecutive trials at 24 and 48 hr AI, respectively. In each trial, a 47°C heat probe was applied at the A7 or A8 segments. A fully recovered larva would produce a stereotypical rolling behavior in response to the heat probe and would be scored as ‘1’, otherwise as ‘0’. If the total score of the three trials was below 1 at 24 hr AI but increased to 2 or 3 at 48 hr AI, the larva was defined as recovered. (B, C) The behavioral recovery test was performed at 24 hr and 48 hr after VNC injury (A7 and A8 bundles). Larvae expressing optoRaf or optoAKT exhibit significantly accelerated recovery in response to light stimulation. (B) Qualification of the total scores at each time point. WT (uninjured) N = 15, WT (light) N = 22, optoRaf (light) N = 32, optoRaf (dark) N = 23, optoAKT (light) N = 26, optoAKT (dark) N = 28. Data are mean ± SEM, analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test. (C) Qualification of the recovery percentage. The data were analyzed by Fisher's exact test, p=0.0230, p=0.7222, p=0.0167, p=1.000. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.