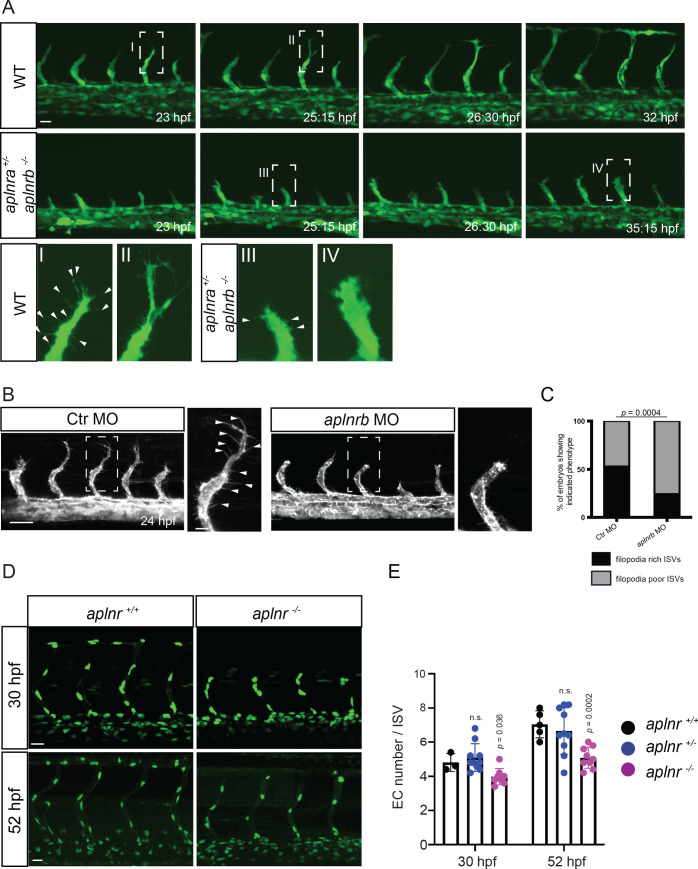
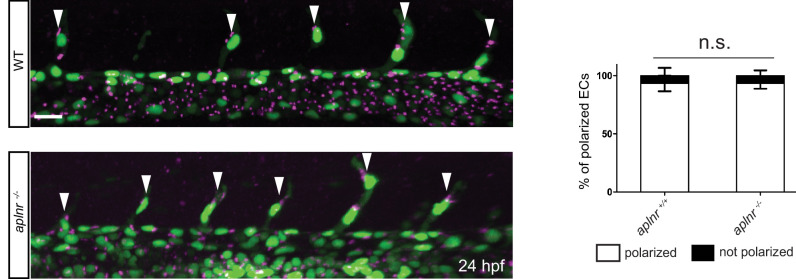
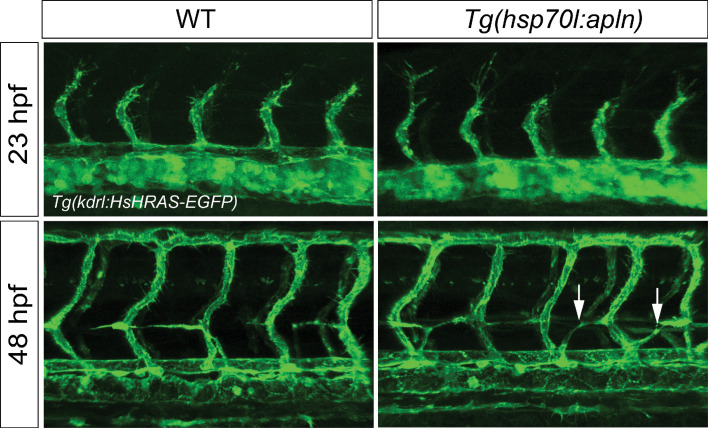
Figure 2. Apelin signaling regulates endothelial filopodia formation and endothelial cell numbers.
(A) Still images from confocal time-lapse movies of vascular development in wild-type and aplnra +/-; aplnrb -/- embryos. During sprouting, wild-type tip cells send out filopodia (arrowheads). aplnra +/-; aplnrb -/- embryos exhibit smaller sprouts and fail to form filopodia. (B) Confocal images of the blood vasculature in 24 hpf Tg(kdrl:HsHRAS-EGFP) embryos injected with Ctr MO and aplnrb MO. aplnrb morphant embryos exhibit smaller sprouts and fail to form filopodia (arrowheads). (C) aplnrb morphant embryos exhibit a reduction in the number of endothelial filopodia (Ctr MO, n = 10; aplnrb MO, n = 15). (D) Confocal images of the blood vasculature of 30 and 52 hpf Tg(fli1a:nEGFP) wild-type and aplnra +/-; aplnrb -/- embryos showing EC cell nuclei. (E) aplnra +/-; aplnrb -/- embryos exhibit reduced EC numbers in the ISVs (30 hpf: aplnr +/+, n = 3; aplnr +/-, n = 10; aplnr -/-, n = 8; 52 hpf: aplnr +/+, n = 5; aplnr +/-, n = 10; aplnr -/-, n = 9). n.s. not significant (two-tailed t-test). Scale bars: A, D, 20 µm; B, 40 µm; B, inset 10 µm.