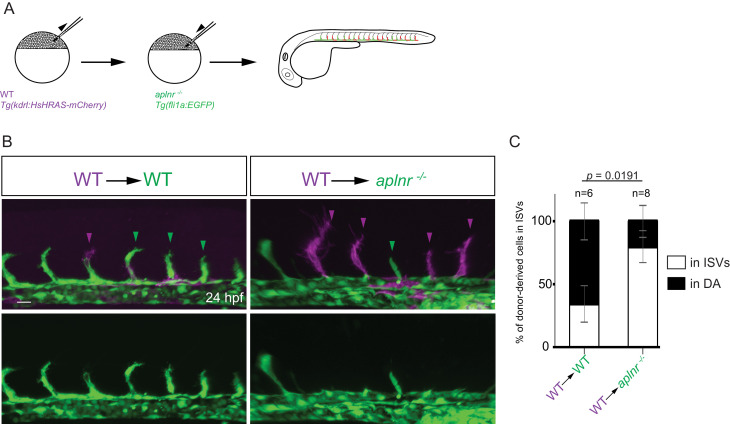
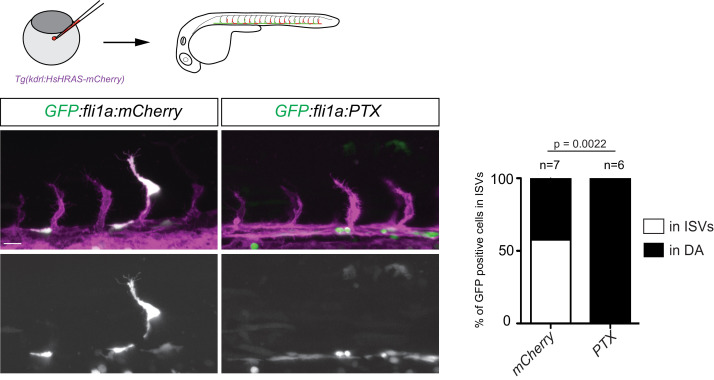
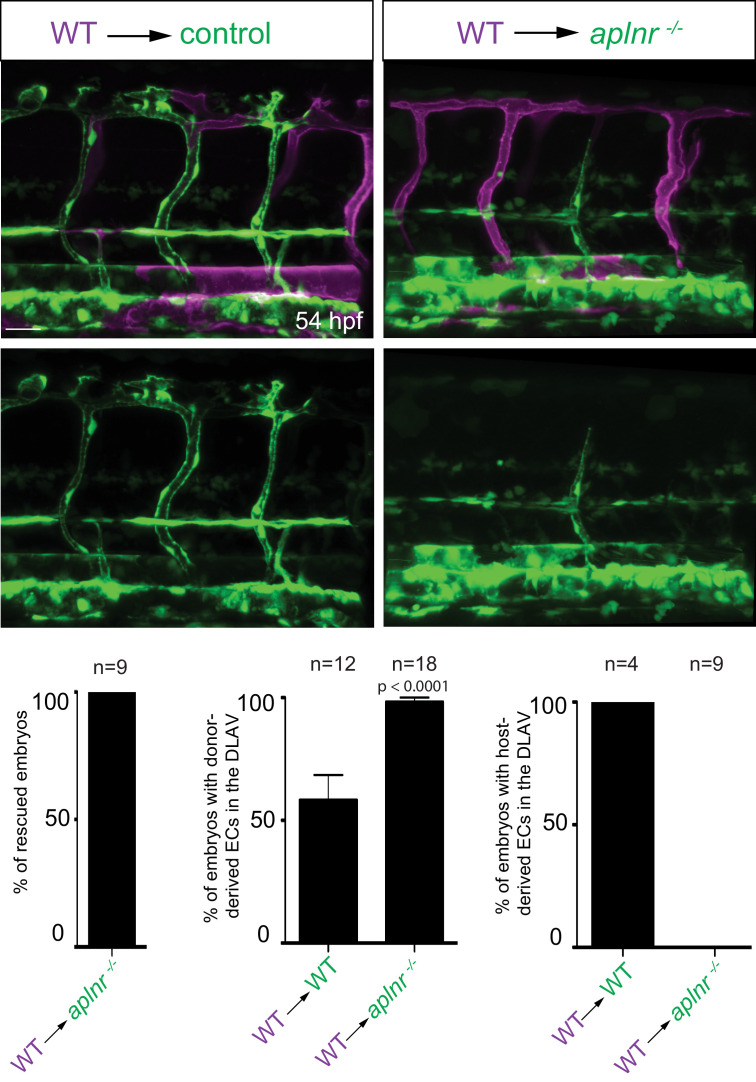
Figure 3. Apelin signaling promotes the sprouting behavior of ECs.
(A) Experimental design: At the blastula stage, cells from Tg(kdrl:HsHRAS-mCherry) embryos were transplanted into host embryos obtained from Tg(fli1a:EGFP) aplnra +/-; aplnrb +/- incrosses. At 24 hpf, the mosaic embryos were imaged and the donor-derived ECs scored for their position. (B, C) 34,5% of wild-type donor-derived ECs in wild-type hosts were found within the ISVs. 80% of wild-type donor-derived ECs in aplnra +/-; aplnrb -/- hosts were found within the ISVs. Notably, wild-type ECs transplanted into aplnr- deficient embryos completely substituted for the lack of cells in the dorsal part of the vasculature at 54 hpf (Figure 3—figure supplement 2). Scale bars: B, 20 µm.