Fig. 4.
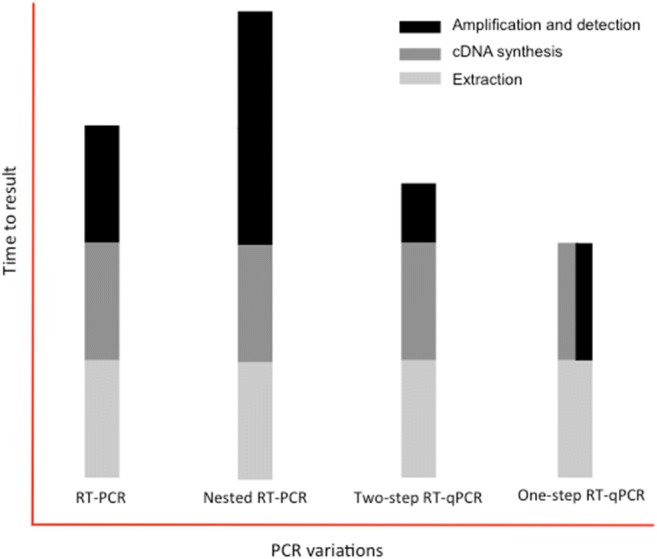
Variations of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) used for virus diagnoses. In conventional PCR after reverse transcription (RT-PCR), the target DNA is detected at the end of PCR amplification, requiring a post-PCR process for visualization (e.g., DNA electrophoresis). The nested RT-PCR significantly enhances the sensitivity of conventional PCR, but it nearly doubles the amplification time. All qPCR protocols detect and measure target DNA after each polymerization (extension) cycle during the exponential amplification through fluorescence and do not require post-PCR processing. While two-step RT-qPCR involves two distinct stages of reverse transcription followed by qPCR, one-step RT-involves a single reaction in which cDNA synthesis and amplification occur successively
