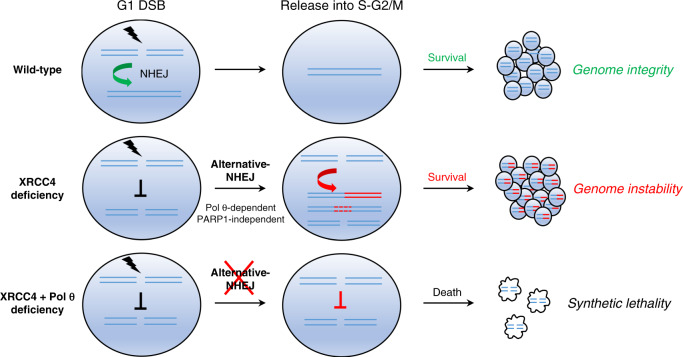
Fig. 6. Model of DSB repair and synthetic lethality in ABL transformed p53-deficient pro-B cells exposed to G1 DNA damage.
Top panel: XRCC4 proficient (wild type) cells repair DSBs in G1 and maintain genome integrity upon release into the cell cycle. Middle panel: XRCC4-deficient cells are unable to repair DSBs in G1. In the absence of p53 G1/S checkpoint, DSBs are repaired in S-G2/M by Pol θ-dependent and PARP1-independent alternative NHEJ that enables cell survival and promotes genomic instability in the form of long DNA resection and chromosomal translocations. Bottom panel: In the absence of XRCC4- and Pol θ-dependent repair, G1 DSBs cause p53-independent cell death due to the accumulation of unresolved DNA breaks in S-G2-M.