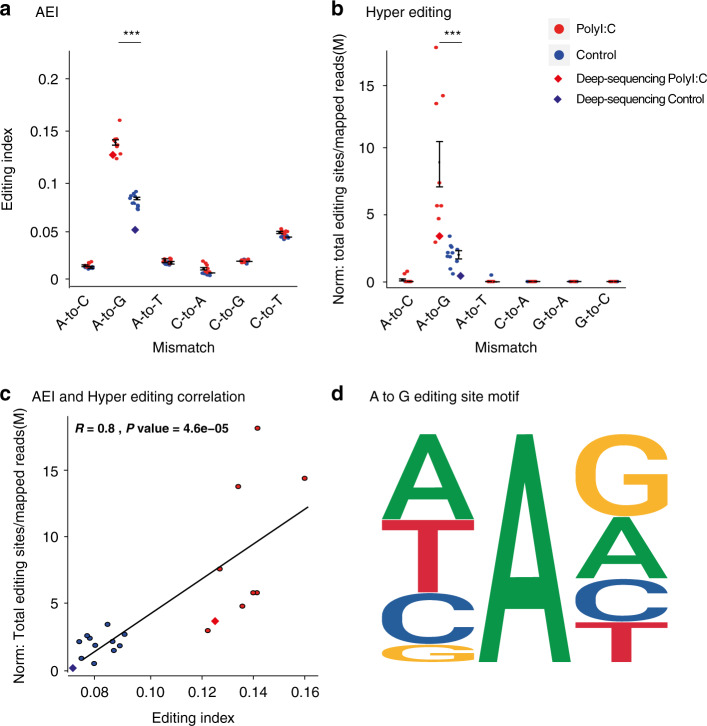
Fig. 3. Increased global levels of A-to-I RNA editing in PolyI:C-treated mice.
Adenosine to inosine, which is read as guanosine (A2G Editing Index), RNA editing levels in PolyI:C mice sequenced on embryonic day 10 analyzed by a Alu Editing Index (AEI) on mouse B1 repetitive elements, and b hyperediting (HE) scheme applied to reads with an extensive editing rate that could not be aligned to the reference genome (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test, p value = 2.6e−05 (W = 88) and 5.29e−05 (W = 87), respectively). Other mismatch types are considered noise. The levels of editing from the deep sequencing samples are indicated with a rhombus. c AEI and HE normalized editing levels are strongly correlated (Spearman, R = 0.8, p value = 4.6e−6). d The familiar ADAR motif signature for the A-to-G sites could be identified. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. All values are means ± SEM.