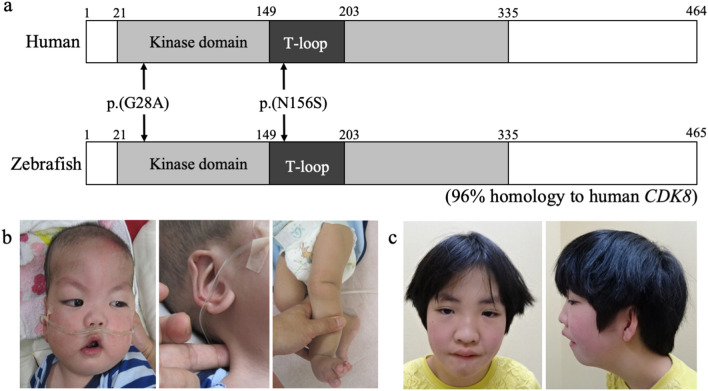
Figure 1.
Schema of the CDK8 protein and clinical characteristics of our two patients with CDK8-associated disorder. (a) Schema of human CDK8 protein (the upper schema) and zebrafish Cdk8 protein (the lower schema). The grey box indicates the kinase domain. The black boxes indicate the T-loop in the kinase domain. The arrows point to the mutations of the 2 reported patients. (b) Patient 1 at 8 months of age. (c) Patient 2 at 8 years of age. In 1b, note the prominent forehead with large anterior fontanelle, arched eyebrow, hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, low-set ears, prominent antihelix, short philtrum, flat nasal bridge, high arched palate, down-turned corners of the mouth, micrognathia, webbed neck, and overlapping toes on the left foot. In 1c, note the hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, wide nasal bridge, protruding ears, bifid uvula, and micrognathia.