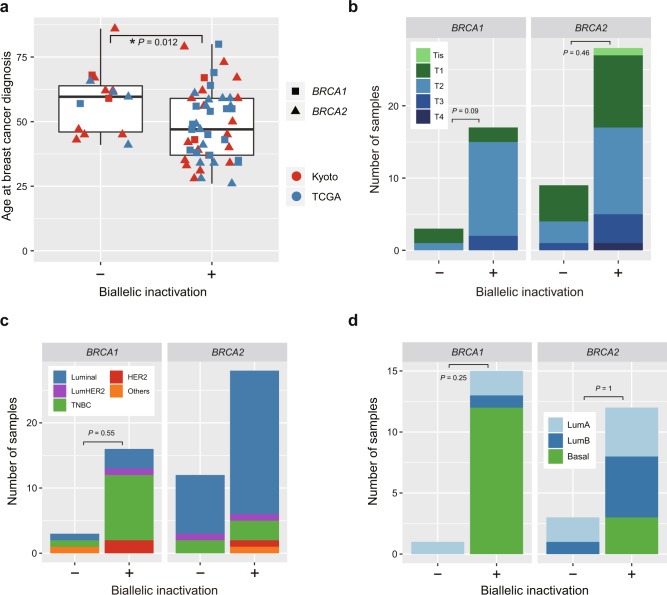
Fig. 4. Phenotypes of breast tumors harboring germline BRCA1/2 mutations with and without biallelic inactivation.
a Age at diagnosis of breast cancers harboring germline BRCA1/2 mutations with (n = 49) and without (n = 15) biallelic inactivation. The asterisk indicates significance difference (Mann–Whitney U test: P < 0.05). b–d Distribution of T factor: (b), in subtypes based on immunohistochemistry (c) in PAM50 mRNA-expression subtypes (d) of breast cancers harboring germline BRCA1/2 variants with and without biallelic inactivation. The difference in frequency of advanced (T2–T4) tumors, triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), and basal-type tumors between tumors with and without biallelic inactivation were tested by the two-sided Fisher’s exact test. Tis carcinoma in situ, LumHER2 luminalHer2, LumA luminalA, LumB luminalB.