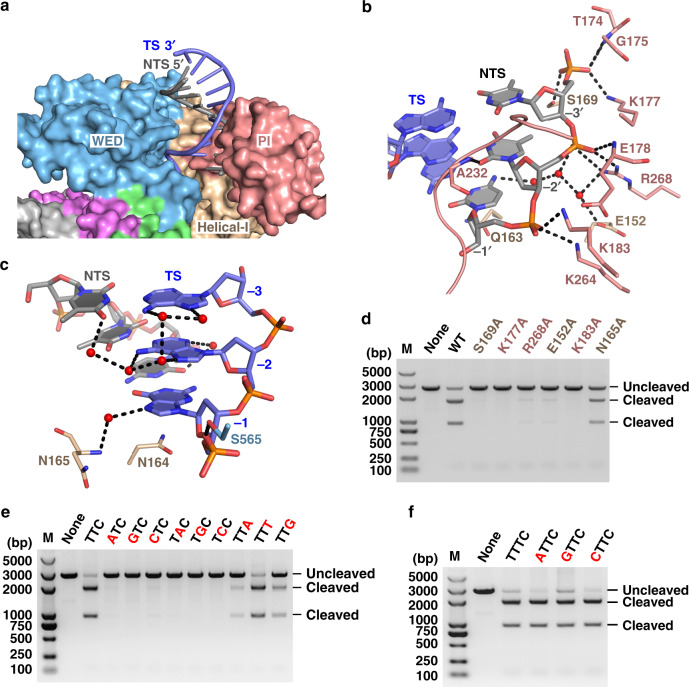
Fig. 3. The PAM duplex recognition.
a Recognition of the PAM duplex by the WED and PI domains. b The PI domain recognizes the base of T(−2′) via Ala232, and forms extensive hydrogen bonds with the phosphate backbone of the non-target strand. c Most bases of the PAM duplex form extensive hydrogen bonds with either Cas12i2 or other bases within the PAM duplex via waters (red spheres), forming a water-mediated hydrogen bond network. d Mutation of residues forming hydrogen bonds with the PAM sequence substantially reduces the DNA cleavage. e DNA cleavage by Cas12i2 using a linear plasmid DNA containing a mutant PAM sequence. The mutated nucleotide is shown in red and the wild-type sequence is shown in black. f The mutation of the nucleotide T that is directly upstream the PAM sequence shows no effect on Cas12i2 DNA cleavage activity.