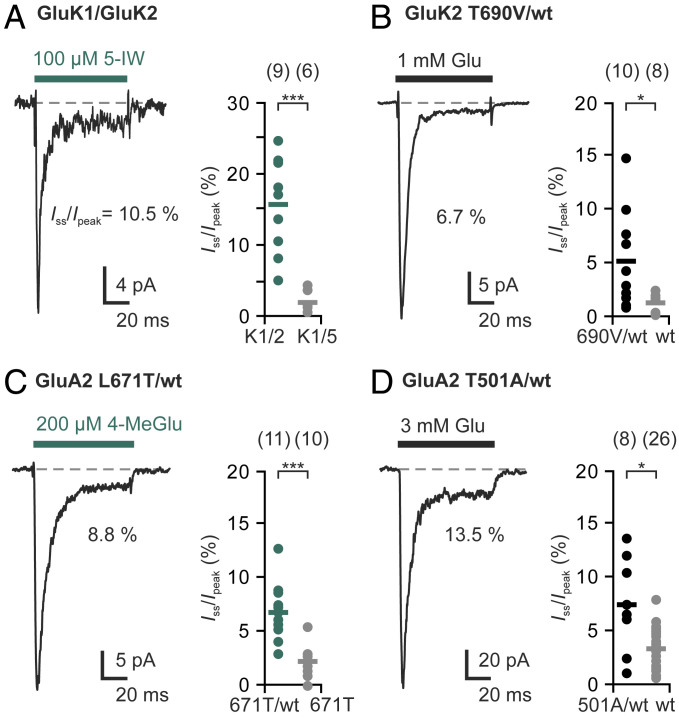
Fig. 4.
Subunit-specific agonists and binding-impaired subunits reduce desensitization of heteromeric kainate and AMPA receptors. (A) Application of the GluK1-specific agonist 5-IW causes significant steady-state currents of GluK1/GluK2 heteromers (green) but not of GluK1/GluK5 heteromers (gray). (B) Incorporation of binding-impaired GluK2(T690V) subunits significantly increases glutamate-induced steady-state currents compared with homomeric GluK2(wt) receptors (gray). (C) GluA2(L671T) is activated by 4-MeGlu, resulting in small steady-state currents that are typical for GluA2 (gray). The 4-MeGlu-induced steady-state currents are significantly higher in heteromers with GluA2(wt) (green). (D) Incorporation of binding-impaired GluA2(T501A) subunits into GluA2 receptors significantly increases glutamate-induced steady-state currents. The bars indicate mean values, and n indicates the number of different patches. Statistical testing was performed with Welch's t tests: *P ≤ 0.05, ***P ≤ 0.001. More details on the experiment and the controls are provided in SI Appendix, Figs. S5–S7.