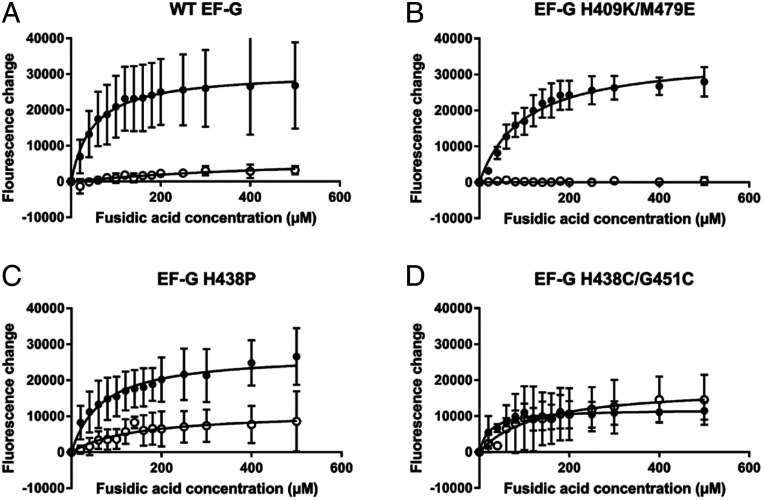
Fig. 4.
The impact of FusB upon accumulation of stalled ribosome:EF-G:GDP:FA complexes. Fluorescence of BODIPY-FL-GDP in response to increasing concentrations of FA in the absence (closed circles) and presence (open circles) of FusB for (A) wild-type EF-G, (B) EF-G H409K/M479E, (C) EF-G H438P, and (D) EF-G H438C/G451C. Data show that, for both wild-type and EF-G H409K/M479E, stalled complexes accumulate in the absence of FusB but little accumulation is observed in the presence of FusB, as FusB promotes dissociation of these complexes. In contrast, for both EF-G H438P and EF-G H438C/G451C, stalled complexes build up in the absence of FusB, similar to the wild-type protein, but both mutant proteins show an increase in fluorescence with increasing FA concentration in the presence of FusB. The large error bars for EF-G H438P mean that a significant difference from wild type cannot be shown with certainty, but the data suggest increased formation of stalled complexes in the presence of FusB. While not restored to levels in the absence of FusB for EF-G H438P, these data show that the H438P and H438C/G451C mutations at least partially restore FA sensitivity in the presence of FusB. This suggests that the changes in dynamics in response to FusB binding that are suppressed by these mutations are important in the mechanism of FusB-induced FA resistance. Each data point represents the mean value after three independent repeats with error bars representing the SD from the mean. For each experiment, n = 15.