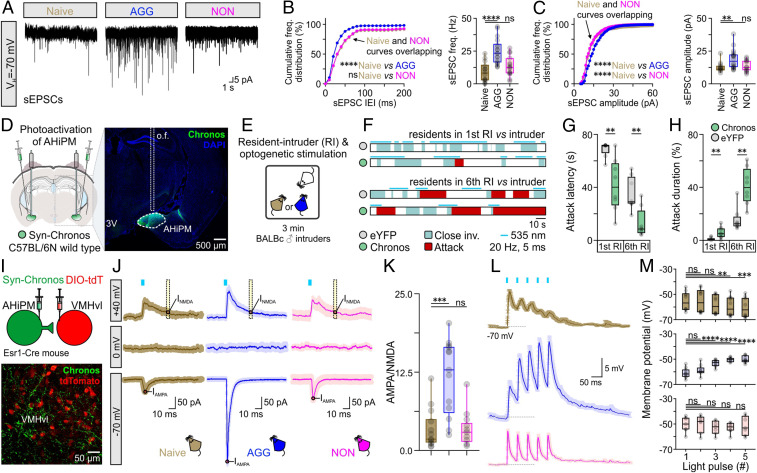
Fig. 2.
AHiPM→VMHvlEsr1 synapses become potentiated following aggression training. (A) Representative recordings of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) from VMHvlEsr1 neurons, from socially naive, AGG, and NON mice. (B, Left) Cumulative frequency distribution plot of sEPSC IEI in voltage-clamp recordings collected from VMHvlEsr1 neurons from socially naive, AGG, and NON mice (n = 14 to 18 VMHvlEsr1 neuron recordings per group, collected from 8 to 10 mice per group, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, P < 0.0001 between socially naive and AGG mice, P = 0.3454 between socially naive and NON mice). (B, Right) Comparison of sEPSC frequency from voltage-clamp recordings collected from VMHvlEsr1 neurons from socially naive, AGG, and NON mice (n = 14 to 18 VMHvlEsr1 neuron recordings per group, collected from 8 to 10 mice per group, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, P < 0.0001 between socially naive and AGG mouse brain slices, P = 0.2576 between socially naive and NON mouse brain slices). (C, Left) Cumulative frequency distribution plot of sEPSC amplitude in voltage-clamp recordings collected from VMHvlEsr1 neurons from socially naive, AGG, and NON mice (n = 14 to 18 VMHvlEsr1 neuron recordings per group, collected from 8 to 10 mice per group, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, P < 0.0001 between socially naive and AGG mice, P < 0.0001 between socially naive and NON mice). (C, Right) Comparison of sEPSC frequency from voltage-clamp recordings collected from VMHvlEsr1 neurons from socially naive, AGG, and NON mice (n = 14 to 18 VMHvlEsr1 neuron recordings per group, collected from 8 to 10 mice per group, Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA with uncorrected Dunn’s post hoc test, P = 0.0041 between socially naive and AGG mouse brain slices, P = 0.6712 between socially naive and NON mouse brain slices). (D, Left) Schematic of the experimental design used for optogenetic studies of aggression following photoactivation of AHiPM. (Right) Confocal image indicative of Chronos-eYFP expression in AHiPM. (E) Schematic illustration of the experimental protocol used in AHiPMChronos stimulation experiments. (F) Sample behavior raster plots with in vivo optogenetics and social behavior in the resident–intruder (RI) assay, of socially naive and AGG mice. (G) Quantification of attack latency, in the first and sixth RI trial (n = 8 mice per group, first RI, two-sided Mann–Whitney U test, P = 0.0033 between YFP and Chronos groups, sixth RI, two-tailed unpaired t test, P = 0.0022 between YFP and Chronos groups). (H) Quantification of attack duration, in the first and sixth RI trial (n = 8 mice per group, first RI, two-sided Mann–Whitney U test, P = 0.0079 between YFP and Chronos groups, sixth RI, P = 0.0011 between YFP and Chronos groups). (I, Top) Schematic of the experimental design used for the study of the AHiPM→VMHvl synapse. (Bottom) Confocal image indicative of AHiPM originating processes in VMHvl. (J) Identification of the AHiPM→VMHvl synapse as purely excitatory, and extraction of the AMPA to NMDA ratio in socially naive, AGG, and NON mice (average of n = 13 to 14 neuron recordings from 8 to 9 socially naive, AGG, and NON mice, respectively). (K) Quantification of the AMPA/NMDA ratio (n = 13 to 14, Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s post hoc test, P = 0.0005 between socially naive and AGG mice, P > 0.9999 between socially naive and NON mice). (L) Synaptic integration in VMHvlEsr1 neurons from socially naive, AGG, and NON mice (average traces of n = 7 to 10 neuron recordings from 7 to 9 mice, respectively). (M) Quantification of the five optically evoked excitatory postsynaptic potentials (oEPSPs) peak amplitude presented in L. (Top) oEPSP amplitude quantification in VMHvlEsr1 neurons recorded from socially naive mice (n = 10 neurons from nine mice, Friedman one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s post hoc test, P > 0.9999 between first and second pulse, P = 0.3587 between first and third pulse, P = 0.0028 between first and fourth pulse, and P = 0.0009 between first and fifth pulse). (Middle) oEPSP amplitude quantification in VMHvlEsr1 neurons recorded from AGG mice (n = 10 neurons from nine mice, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, P = 0.2935 between first and second pulse, P < 0.0001 between first and third pulse, P < 0.0001 between first and fourth pulse, and P < 0.0001 between first and fifth pulse). (Bottom) oEPSP amplitude quantification in VMHvlEsr1 neurons recorded from NON mice (n = 7 neurons from seven mice, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, P = 0.9865 between first and second pulse, P = 0.5704 between first and third pulse, P = 0.0751 between first and fourth pulse, and P = 0.9803 between first and fifth pulse). ns, not significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. In box plots, the median is represented by the center line, the interquartile range is represented by the box edges, the bottom whisker extends to the minimal value, and the top whisker extends to the maximal value. VH, holding voltage; IEI, inter-event interval, o.f., optic fiber; DIO-tdT, Cre-dependent tdTomato expression.