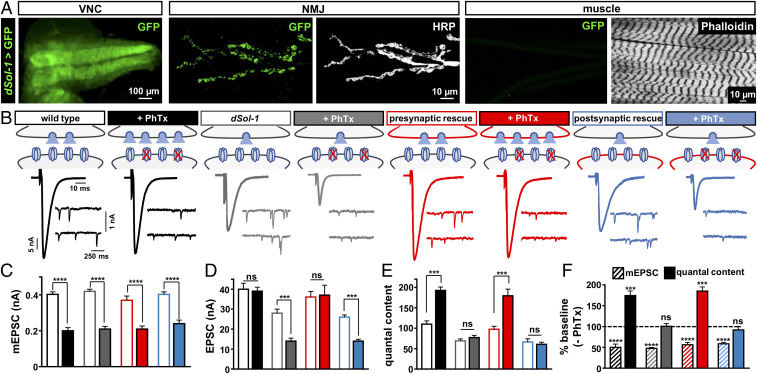
Fig. 3.
Presynaptic dSol-1 expression is necessary to promote basal neurotransmitter release and homeostatic potentiation. (A) Representative larval ventral nerve cord (VNC) and NMJ images of GFP expression driven by the dSol-1 promoter and amplified with a Gal4-inducible tubulin-Gal4 cassette (w;dSol-1-Gal4/Tub-FRT-STOP-FRT-Gal4,UAS-FLP,UAS-CD8-GFP). Anti-HRP (neuronal membrane marker) and anti-phalloidin (muscle actin marker) are shown. dSol-1 is exclusively expressed in the nervous system with no detectible signal in the muscle. (B) Rapid expression of PHP requires dSol-1. Representative EPSC and mEPSC traces for wild type, dSol-1bk1 mutants, presynaptic rescue (neuronal expression of dSol-1 in dSol-1 mutants; w;OK6-Gal4/UAS-dSol-1;dSol-1bk1), or postsynaptic rescue (muscle expression of dSol-1 in dSol-1 mutants; w;G14-Gal4/UAS-dSol-1;dSol-1bk1) at baseline and after PhTx application. Presynaptic expression of dSol-1 fully restores PHP expression, while PHP fails in the postsynaptic rescue condition. (C–E) Quantification of mEPSC amplitude (C), EPSC amplitude (D), and quantal content (E) values at baseline and after PhTx treatment. (F) Quantification of mEPSC amplitude and quantal content values following PhTx application relative to baseline (−PhTx) in the indicated genotypes. Error bars indicate ±SEM. ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. Absolute values for normalized data are summarized in SI Appendix, Table S2.