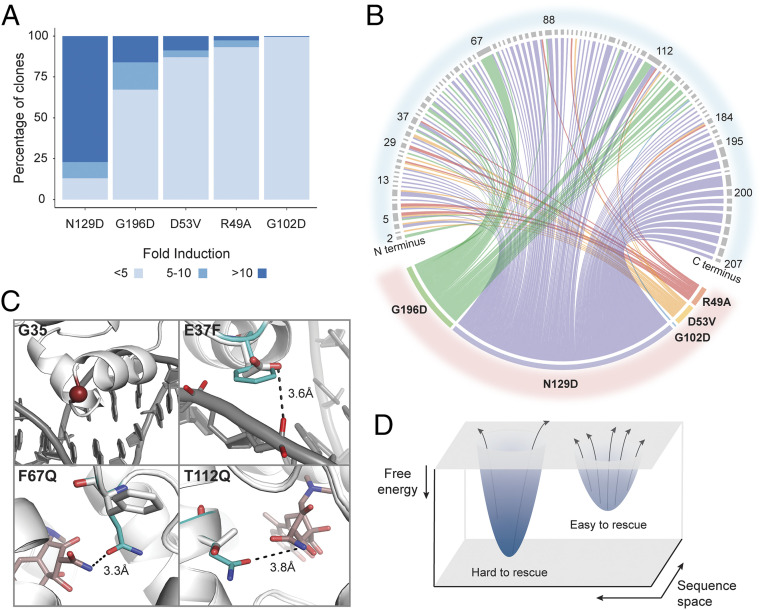
Fig. 2.
Site-specific differences and structural mechanisms of rescue of function. (A) Percentage of rescued clones whose allosteric activity, based on fold induction, is strong (>10), moderate (5–10), or inactive (<5). (B) Distribution of rescuing mutations (Upper) for each dead variant (Lower) shown in different colors. Each line connects dead and rescuing variants, and its thickness represents number of rescuing mutations at that position. (C) Rosetta structural models of LBD and DBD rescue mutations. Potential common mechanisms of rescue include weaker interaction between DBD and DNA (G35 and E37F) or stronger interactions between LBD and ligand (F67Q and T112Q). (D) Free energy landscape hypothesizing relationship between rescuability and energy gap between inactive and active states. Larger gap (deeper well) is harder to rescue than smaller gap (shallower well).