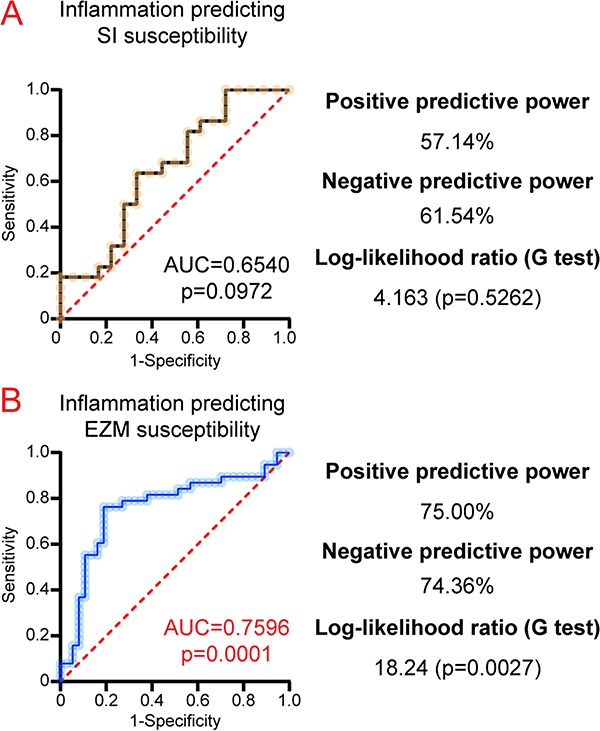
Fig. 5.
A specific subset of peripheral inflammatory proteins are more predictive of EZM-determined susceptibility than SI-determined susceptibility. Mice were run through the 10-day RSDS paradigm followed by behavioral testing, plasma extraction, and inflammation assessment by Meso Scale Discovery multiplex analysis. A. Receiver-operating characteristics (ROC) curves were generated for select inflammatory parameters (IL-2, IL-10, IL-17A, IL-22, and TNFα) predicting social interaction (SI) susceptibility. B. ROC curves generated for select inflammatory parameters (IL-2, IL-10, IL-17A, IL-22, and TNFα together) predicting elevated zero maze (EZM) susceptibility. Prediction ability was calculated by area under curve, with p-value calculated by a two-tailed test with predicted probability of each subject set at 0.5. Goodness-of-fit additionally assessed by Log-likelihood ratio.