Figure 1 |. Protective vs non-protective glucose metabolism in human islets undergoing inflammation and attendant metabolite signatures.
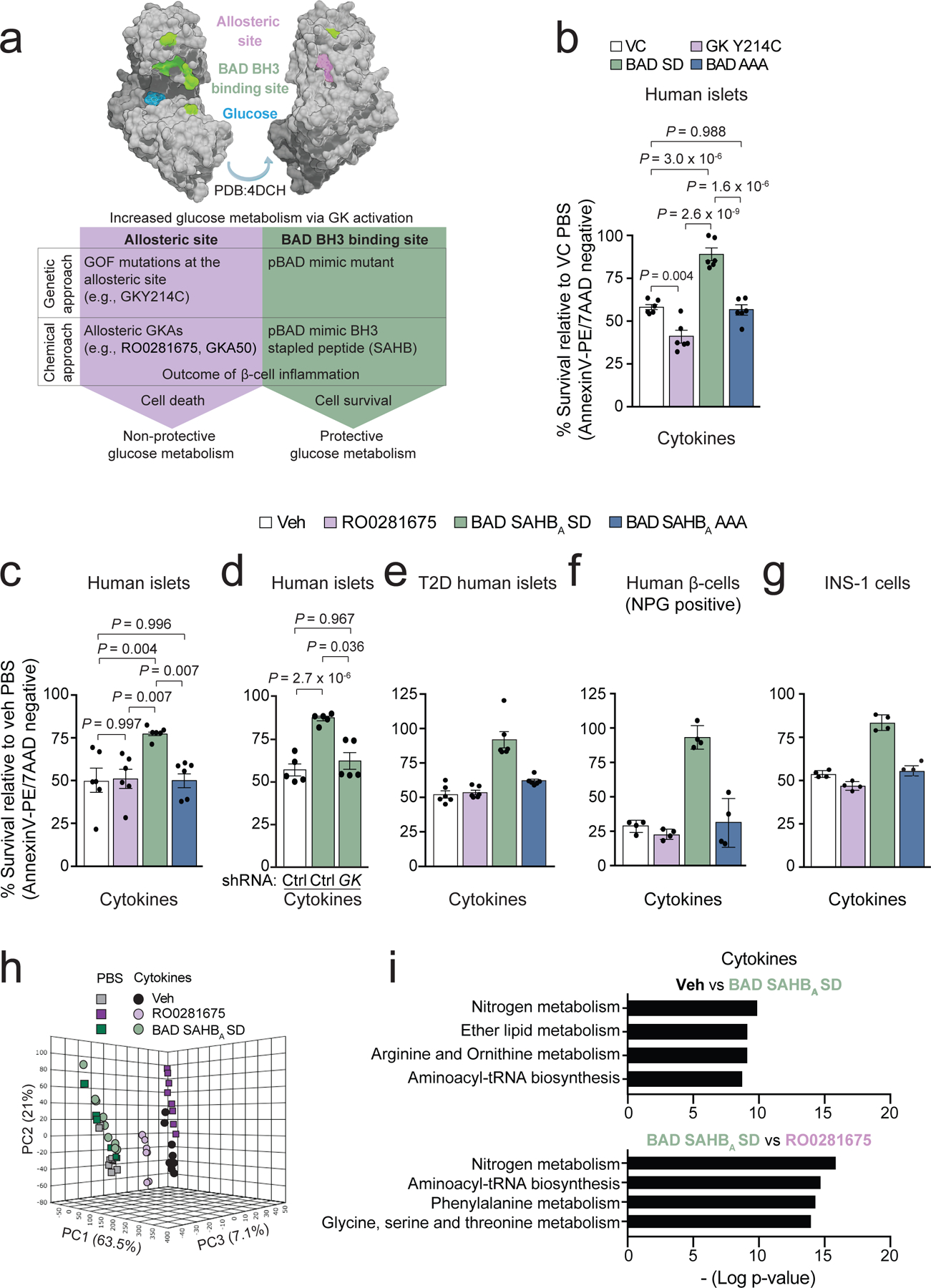
a, Schematic summary showing modelling of protective versus non-protective glucose metabolism using GK-targeted genetic and pharmacologic tools. GOF denotes gain-of-function.
b, Viability of human islets expressing vector control (VC), GK Y214C, BAD SD, or BAD AAA following 48 h treatment with a cocktail of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IFNγ). Values are normalized to VC PBS control treatment. Data are from n=3 human donors each with 2 replicates.
c, Viability of human islets treated with vehicle (Veh, DMSO), RO0281675, BAD SAHBA SD or BAD SAHBA AAA and exposed to cytokines for 48 h as in (b), n=6 donors.
d, Viability of human islets subjected to GK knockdown and treated with vehicle or BAD SAHBA SD in the presence of inflammatory cytokines. Data are from n=5 independent experiments using islet cultures from 2 donors.
e, Viability of T2D donor islets treated as in (c). Data are from n=2 independent experiments using islet cultures from 2 donors.
f, Viability of β-cells within human islets treated as in (c) and visualized by co-staining with Newport Green (NPG) and AnnexinV/7AAD. Data are means ± s.d. from n=4 technical replicates of islets cultures from one donor.
g, Viability of INS-1 β-cells treated as in (c). Data are means ± s.d. from n=4 technical replicates.
h, Principal component analysis (PCA) of LC-MS untargeted metabolomics of human islets treated as in (c) for 24 h, n=5 donors pooled and split into 8 replicates for metabolomics analysis.
i, Pathway analysis displayed as bar plot showing pathway -log p-values, revealing nitrogen, arginine and ornithine metabolism as the top pathways changed in vehicle control versus BAD SAHBA SD or in RO0281675 versus BAD SAHBA SD comparisons, n=5 donors. For RO0281675 vs. BAD SAHBA SD comparisons, arginine and ornithine metabolism is not displayed but is statistically enriched with a P-value of 1.21 × 10−8.
Data in b–d and i are means ± s.e.m. with statistical analyses on means from independent experiments using one-way ANOVA with Tukey adjustment for multiple comparisons.
