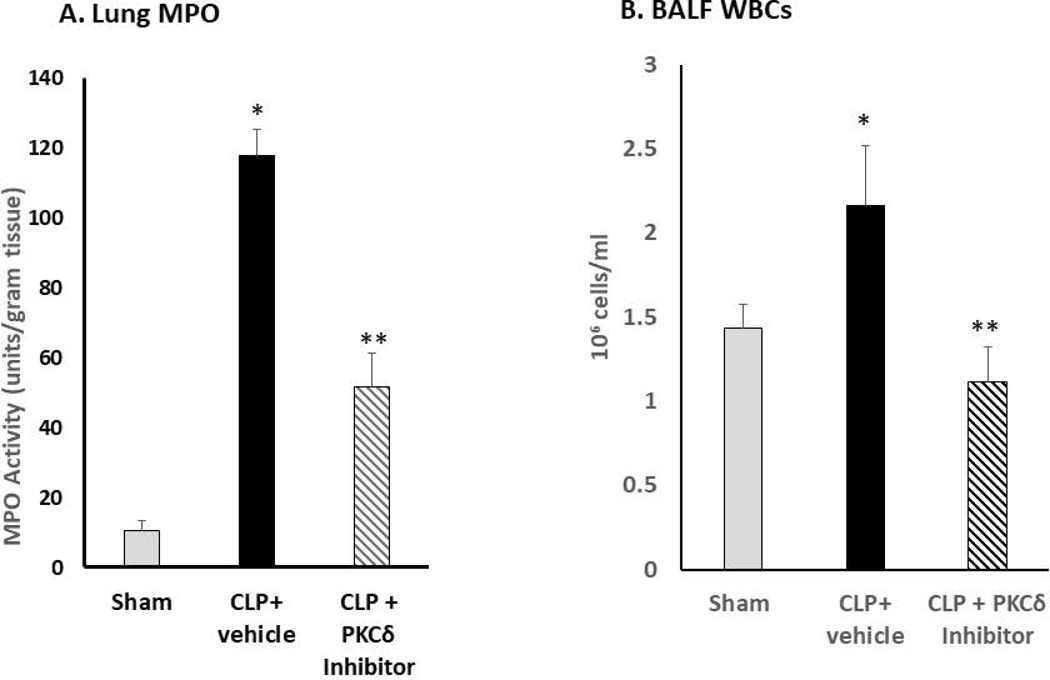
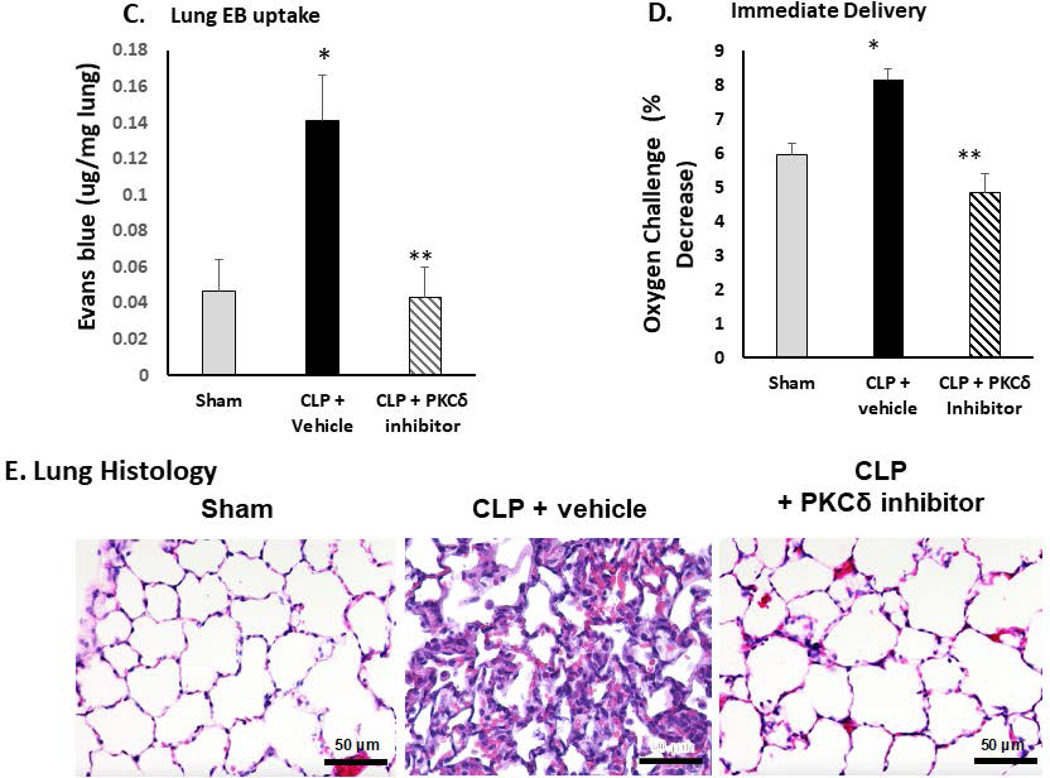
Figure 1: PKCδ inhibition reduces neutrophil influx and attenuates acute lung injury in sepsis.
A. PKCδ inhibition attenuates pulmonary Myeloperoxidase activity in sepsis. Pulmonary myeloperoxidase activity was measured 24 hr post sham or CLP surgery in lung tissue homogenates obtained from rats administered IT vehicle or PKCδ inhibitor (200ug/kg). *P< 0.01 Sham vs. CLP+ Vehicle, **P<0.05 CLP+ vehicle vs. CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor, n= 4 rats/group. B. PKCδ inhibition decreases WBC in the BALF in sepsis. White blood cell counts were analyzed in the BAL fluid at 24 hr post sham or CLP surgery in rats administered with the vehicle or the PKCδ inhibitor. BALF cells were counted using a Hemavet® Multispecies Hematology System (*p < 0.05 Sham vs. CLP+Vehicle, ** P<0.03 CLP+Vehicle vs. CLP+PKCδ inhibitor, n=5 rats/group). C. PKCδ inhibition decreases lung permeability in sepsis. Lung vascular permeability was determined by Evans blue dye uptake into the lung at 24 hr post sham or CLP surgery in rats administered with the vehicle or the PKCδ inhibitor. *P< 0.05 Sham vs. CLP+ Vehicle, **P<0.05 CLP+ vehicle vs. CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor, n= 3–4 rats/group. D. PKCδ inhibition improves lung function in sepsis. Oxygen Reserve was determined by performing an oxygen challenge and measuring oxygen saturation 24 hr post-surgery in Sham, CLP+ vehicle and CLP+PKCδ inhibitor treated rats who were serially exposed to FiO2 = 1 and then 0.40 for 5 min intervals with the difference between the final SpO2 between these oxygen conditions representing oxygen reserve under resting conditions. * P≤ 0.001 Sham vs. CLP+ Vehicle, ** P<0.001 CLP+ vehicle vs. CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor, n= 5 rats/group. E. PKCδ inhibition is lung protective and attenuated histologic changes in the lung associated with CLP-induced sepsis. H&E staining in representative lung tissue sections from 24 hours after surgery (minimum of 4 animals per group). Sham-surgery; lung architecture was normal, with open alveoli and thin alveolar walls. CLP+vehicle; sepsis-induced severe indirect lung injury evidenced by a loss of lung architecture, marked inflammatory infiltrate, thickening of alveolar walls and septa, visible hemorrhaging and proteinaceous exudate filling alveoli. CLP + PKCδ inhibitor; PKCδ inhibition attenuated sepsis-induced lung injury, evidenced by preservation of lung architecture, reduced inflammatory infiltrate, maintenance of alveolar wall thickness, and reduction of hemorrhaging and proteinaceous exudate induced by sepsis. Scale bars: 50 μm. Original magnification: 400x.