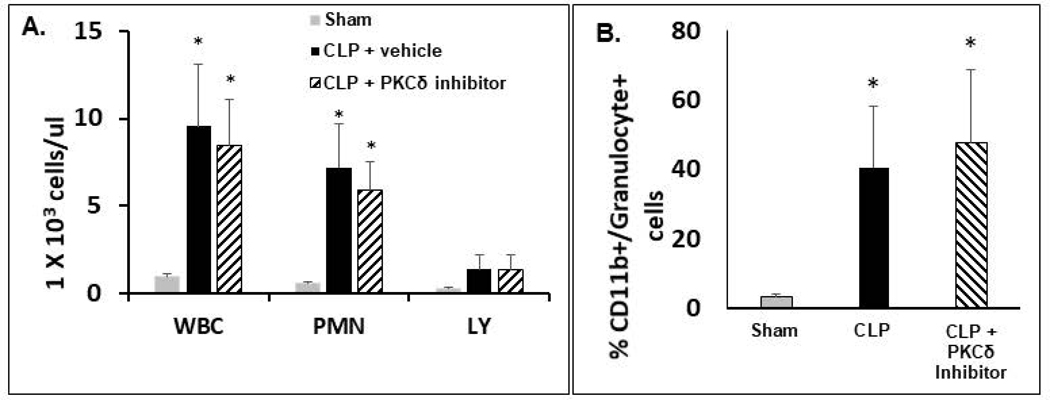
Figure 4: PKCδ inhibition does not alter sepsis-induced immune cell recruitment to the peritoneal cavity.
A.-B.: Peritoneal cells were isolated from the PCF of Sham, CLP+ Vehicle and CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor treated rats 24 hr post-surgery. A: Total WBCs, neutrophil, and lymphocyte counts in peritoneal cavity fluid. Values are expressed as 1×103 cells/μL. *p<0.05 Sham vs. CLP+ Vehicle and Sham vs. CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor mice, n = 5–6 rats/group. B: Cells harvested from the peritoneal cavity were analyzed by flow cytometry. Activated neutrophils are shown as the percentage of cells double positive for CD11b and the rat granulocyte marker (clone RP-1). *P<0.05 Sham vs. CLP+ vehicle and Sham vs. CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor, n= 3 rats/group.