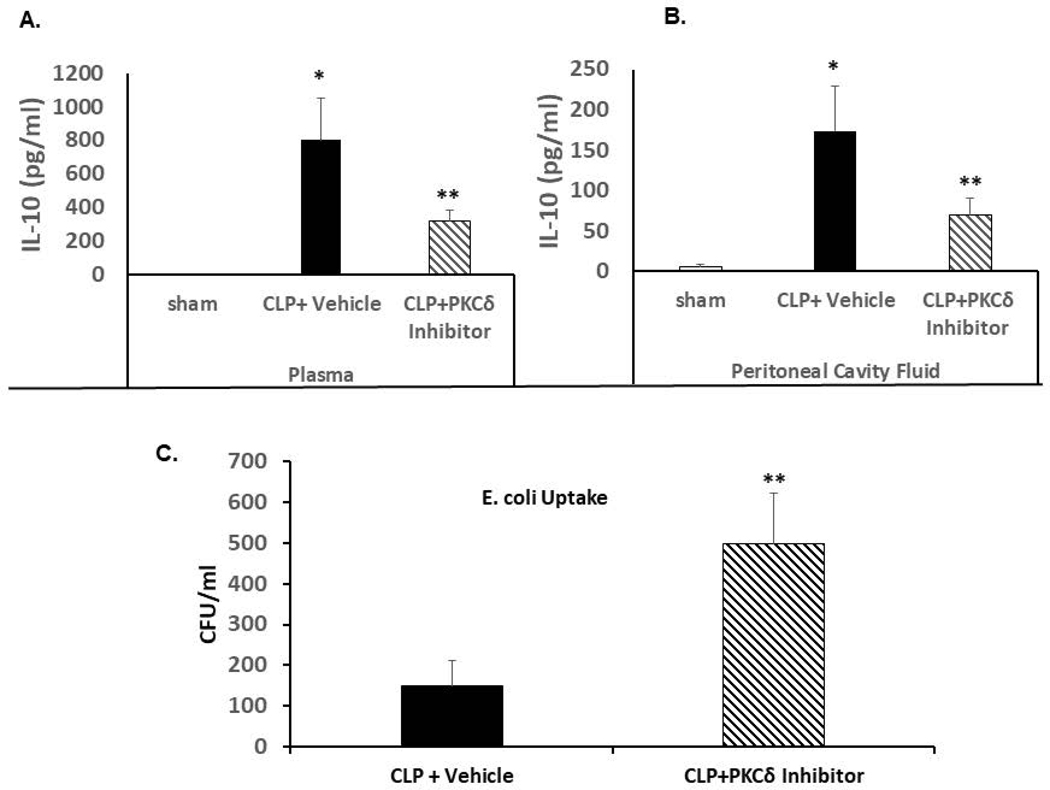
Figure 5: PKCδ inhibition attenuates sepsis-increased levels of IL-10 in the plasma and peritoneal cavity fluid and increases peritoneal macrophage phagocytosis ex vivo.
A. IL-10 levels were determined in plasma isolated from Sham, CLP+ Vehicle and CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor treated rats 24 hrs post-surgery. *P<0.001 Sham vs. CLP+ vehicle, **P<0.03 CLP+ vehicle vs. CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor (n=12). B. IL-10 levels in the peritoneal cavity fluid *P<0.001 Sham vs. CLP+ vehicle, **P<0.03 CLP+ vehicle vs. CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor (n=6). C: Peritoneal macrophages were isolated 4 hrs post CLP surgery in rats treated with vehicle (PBS) or the PKCδ inhibitor after CLP surgery. Isolated macrophages were incubated with E. coli and bacterial phagocytosis was determined as described in Methods. Bacteria levels are expressed as colony forming units (CFU)/ml. *P<0.05 CLP+ vehicle vs. CLP+ PKCδ inhibitor (n=3 rats/group)