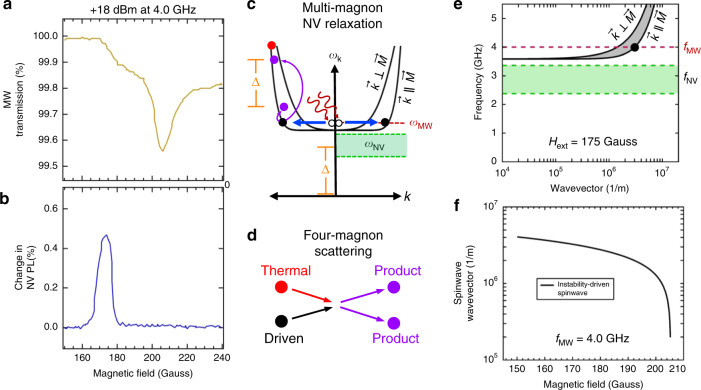
Fig. 4. NV detection of spinwave instability in the multi-magnon NV relaxation regime.
a Microwave absorption during a static magnetic field sweep at 4.0 GHz and +18 dBm microwave power shows a uniform mode FMR absorption signal at 206 Gauss and an instability shoulder at lower field. b Simultaneously collected NV signal shows relaxation only at the lowest field where the instability is excited, and NV relaxation is minimal at the uniform mode FMR condition. c At these magnetic fields, the minimum of the spinwave manifold is lifted to higher frequency than the NV states, and there are no NV resonant magnons possible. An increase in NV-resonant magnetic field noise from multiple magnons generated in the four magnon scattering process (d) leads to a change in NV PL. e Calculated spinwave manifold (gray) and NV center frequency range (green) at 175 Gauss gives the wavevector of the 4.0 GHz instability-driven magnon (3.2 × 106 m−1, black circle). f Calculated wavevector of 4.0 GHz instability-driven spinwave as a function of magnetic field.