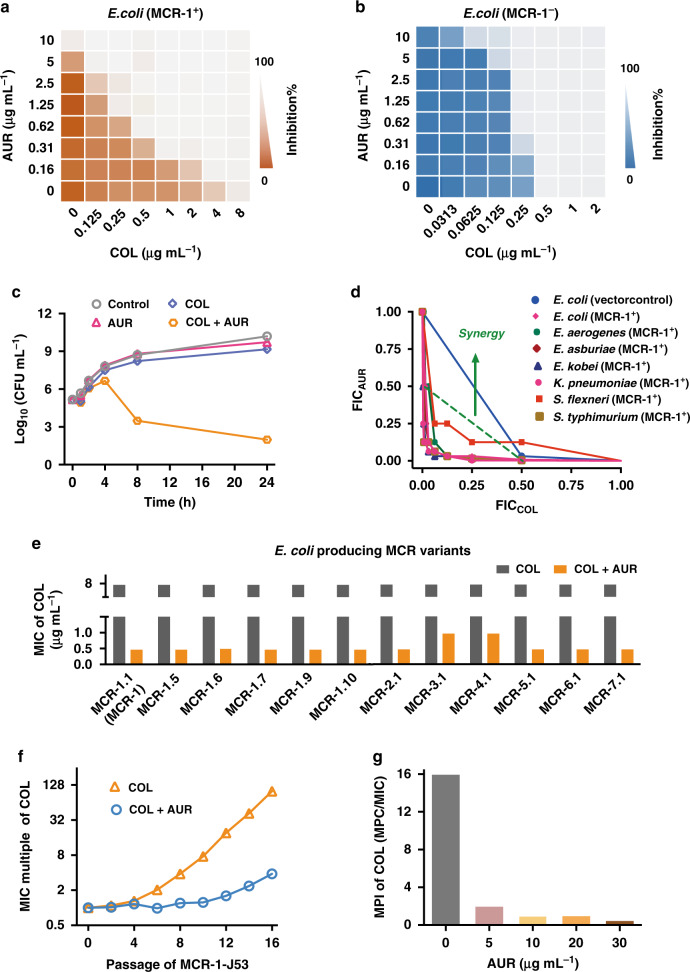
Fig. 4. Auranofin synergizes with colistin to kill MCR-positive bacterial strains.
a, b Representative heat plots of microdilution checkerboard assay for the combination of COL and AUR against a MCR-1-positive E. coli and b MCR-1-negative E. coli. c Time-kill curves for COL and AUR monotherapy or combination therapy against MCR-1-J53 during 24-hr incubation. The concentrations of COL and AUR are 2 μg·mL−1 and 6 μg·mL−1, respectively. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM, n = 3 biologically independent samples. d Isobolograms of the combination of COL and AUR against different MCR-1-positive bacterial strains. The green dash line indicates ideal isobole, where drugs act additively and independently. Data points below this line indicate synergism. e Bar charts showing the reduction of COL MIC for E. coli J53 that produced MCR-1 variants and MCR homologs in the combined use with AUR at fixed concentration of 0.625 μg·mL−1. f Resistance acquisition curves during serial passage with the subinhibitory concentration of COL or the combination of COL and AUR against MCR-1-J53. MIC test was performed every two passages. g Bar charts showing MPI indices of MER in the presence of increasing concentration of AUR against MCR-1-J53. a, b Data in a and b represent the mean OD600 of two biological replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.