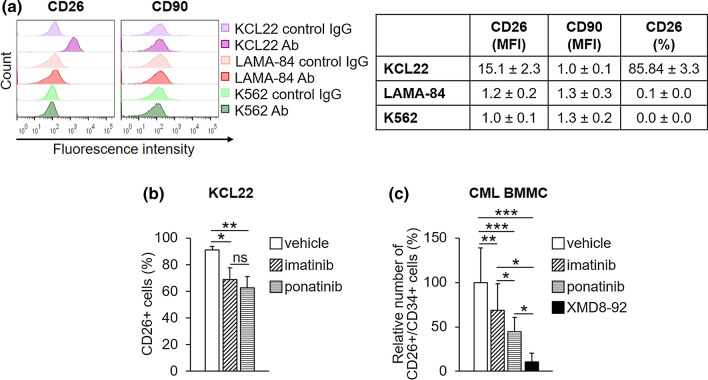
Fig. 3.
Effects of TKi on CD26-expressing CML cells. a The expression of CD90 and CD26 cell surface antigens in routinely cultured cells was assessed by flow cytometry using specific antibodies (Ab). Cell mean fluorescence intensity (MFI), calculated using matched-isotype IgG as negative control (control IgG), and the percentages of CD26-expressing cells obtained from the same experiments are reported in the table. Values represent mean ± SD of data obtained from three independent experiments. b KCL22 cells (3 × 105/mL) were treated with DMSO (vehicle), 1 μM imatinib or 4 nM ponatinib at time 0 and incubated for 72 h. Histograms relative to the average percentages of KCL22 cells expressing CD26 from three independent experiments (mean ± SD) are shown. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ns not significant. c Patient-derived CML cells (3 × 105/mL) were treated with DMSO (vehicle), 1 μM imatinib, 4 nM ponatinib or 10 μM XMD8-92 at time 0 and incubated for 72 h. Histograms relative to the average percentages of CD26/CD34-expressing cells from three patients (mean ± SD) are shown. See Supplementary Fig. S1b for single patient data in the electronic supplementary material. CML chronic myeloid leukemia, DMSO dimethyl-sulfoxide, TKi tyrosine kinase inhibitors; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001