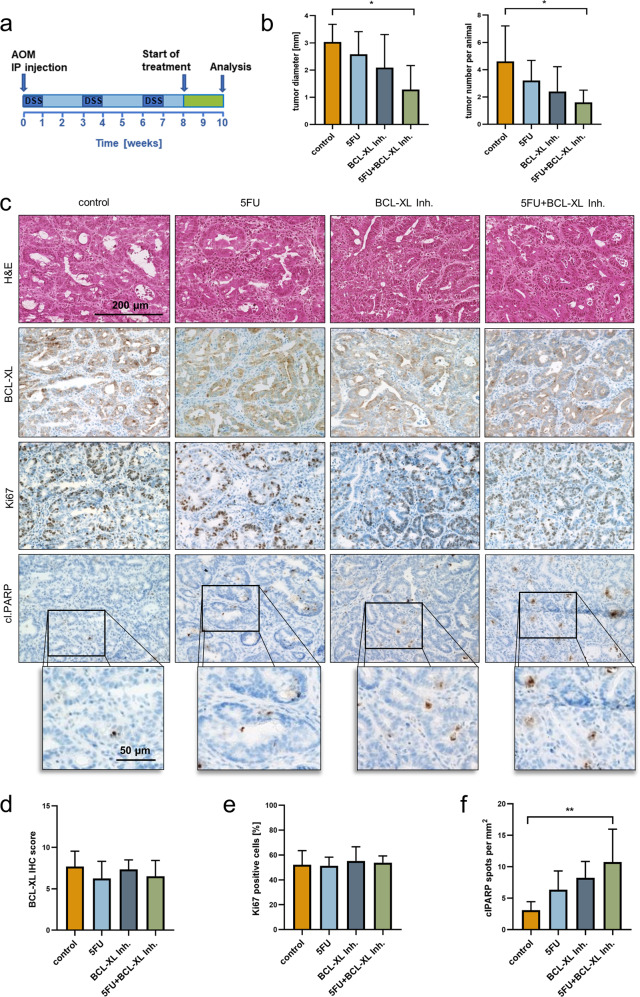
Fig. 4. Selective BCL-XL inhibition is effective in the treatment of tumors in a murine CRC model.
a Schematic time course with a tumor initiation and a treatment phase. Initiation: intraperitoneal injection of azoxymethane (AOM) at the start day and three cycles of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) in the drinking water (2% w/v). Treatment: 25 mg/kg A-1331852 (orally available BCL-XL inhibitor) daily by oral gavage or 3x per week 30 mg/kg 5FU by intraperitoneal injection for a total time period of 14 days. b Tumor sizes (left graph) and numbers (right graph) in mice after treatment with A-1331852, 5FU, the combination of both or the respective solvents as a control (n = 5 animals per group). c Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining (upper panel) and immunohistochemical staining against BCL-XL, Ki67 (proliferation marker) and cleaved PARP (cl.PARP; apoptosis marker) on tumors derived from animals treated as depicted in a. Scale bars as indicated d Scoring of the IHC staining of BCL-XL depicted in c. e Percentage of Ki67-positive cells, referred to Hematoxylin stained nuclei. f Number of cl.PARP positive spots per mm2. Results in b, d, e, and f are shown as mean with standard deviation; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.