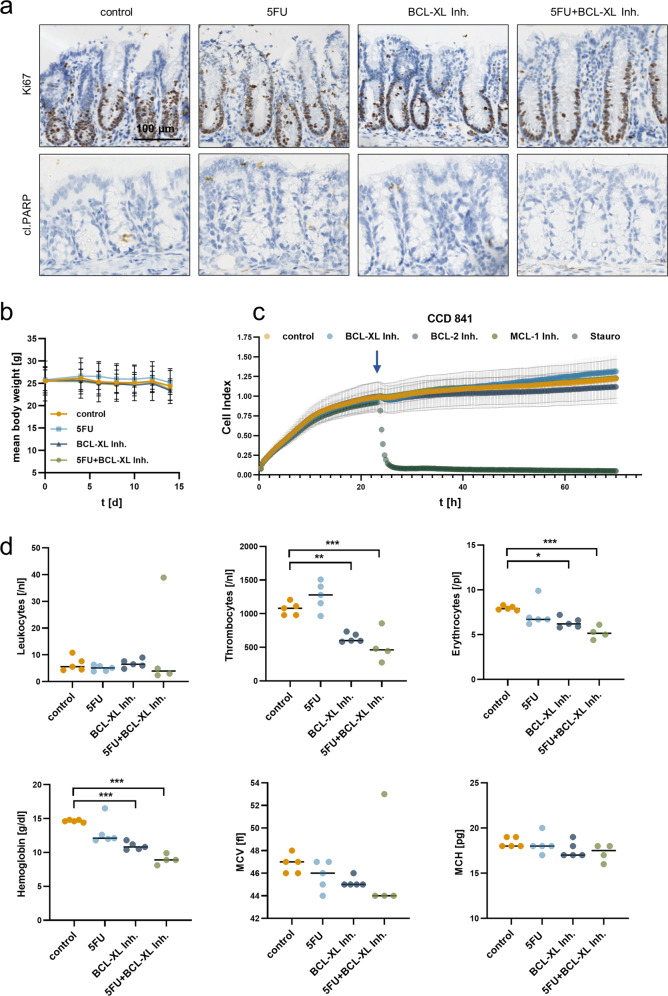
Fig. 5. Selective BCL-XL inhibition does not induce cell death in intestinal epithelial cells.
a Immunohistochemical staining against Ki67 (proliferation marker) and cleaved PARP (cl.PARP; apoptosis marker) on longitudinal sections of colon crypts, derived from animals treated as depicted in (4a). Scale bar indicates 100 µm. b Body weight alterations during the course of treatment. c Impedance monitoring of human intestinal epithelial cell line CCD 841 CoN for 72 h. After 24 h (blue arrow), cells were treated with 20 µM of WEHI-539 (BCL-XL inhibitor), S63845 (MCL-1 inh.) or ABT-199 (BCL-2 inh.). DMSO was used as vehicle control and 2 µM Staurosporine (Stauro) as positive control for cell death induction. Results are shown as mean ± standard deviation; n = 3. d Small hemogram from mice after indicated treatment. MCV mean corpuscular volume, MCH mean corpuscular hemoglobin. Results are shown as median; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.