Fig. 1.
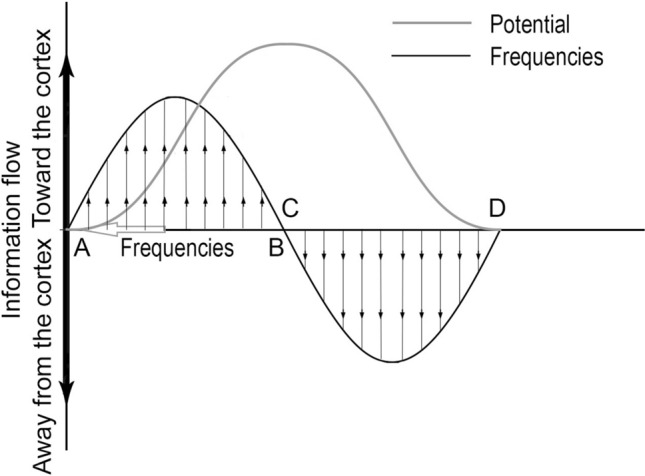
Changes in energy balance due to the stimulus. The brain frequencies change from high, on the left (A), to low, toward the right (D), determining the direction of information flow in the brain (shown by thin arrows). The resting state of the brain is energy neutral before stimulus (A) and after a response (D). The first part of the cycle (AB) is driven by the stimulus, whereas the evoked potential restores the resting state via self-regulation (CD). The enhanced brain frequencies represent high temperature and robust energy need; the low frequencies expand by forming high amplitude, which correlates to a cooling down Adapted from Deli et al. 2018)
