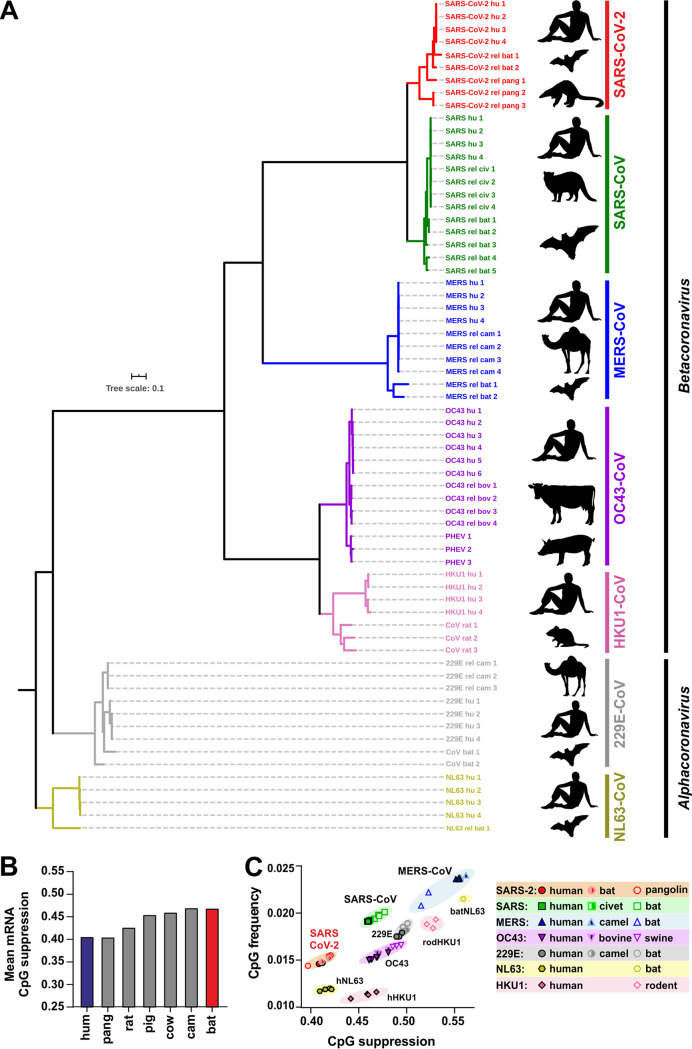
FIG 1.
Phylogenetic relationship between human coronaviruses and their animal relatives and CpG suppression in pathogens and their hosts. (A) Distance-based relationship inference based on representative full-genome nucleotide sequences of human-infecting SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, HKU1-CoV, OC43-CoV, NL63-CoV, and 229E-CoV strains and their closest known animal relatives. Black symbols to the right indicate the viral host (human, horseshoe bat, pangolin, civet, camel, rat, pig, or cattle). (B) Mean CpG suppression (i.e., number of observed CpGs normalized to expected CpGs based on sequence length and GC content) in mRNAs of the indicated host species (human [hum], pangolin [pang], rat, pig, cow, camel [cam], or horseshoe bat [bat]). (C) CpG frequency (number of CpGs normalized to sequence nucleotide length) and suppression (number of observed CpGs normalized to expected CpGs based on sequence length and GC content) in human coronavirus genomes and their closest animal-infecting relatives.