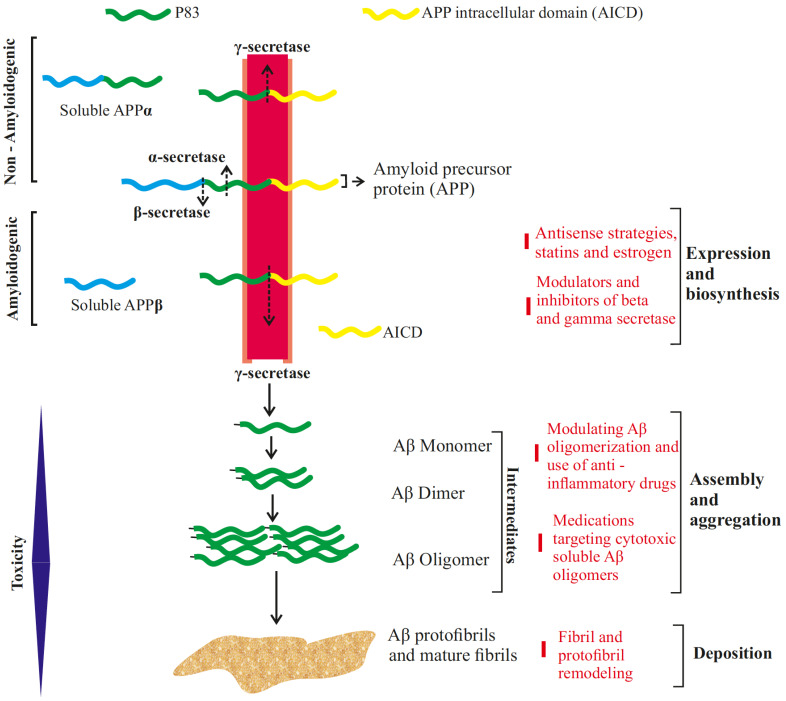
Fig. (1).
Beta-amyloid treatment strategies at various levels of its maturation. The non-amyloidogenic pathway results in the sequential cleavage of transmembrane Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) by the enzymes α-secretase and γ-secretase resulting in soluble APPα fragment, P83 fragment (proteolytically degraded at later stages) and APP Intracellular Domain fragment (AICD). In amyloidogenic pathway, APP is first processed by β-secretase, releasing soluble APPβ, followed by γ-secretase which cleaves the remaining fragment generating either Aβ1-40 or Aβ1-42, the length of which is determined by the site at which γ-secretase cuts. These Aβ monomers assemble together in series of steps, forming dimers to cytotoxic oligomers, developing into protofibrils and mature fibrils. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).