Figure 1.
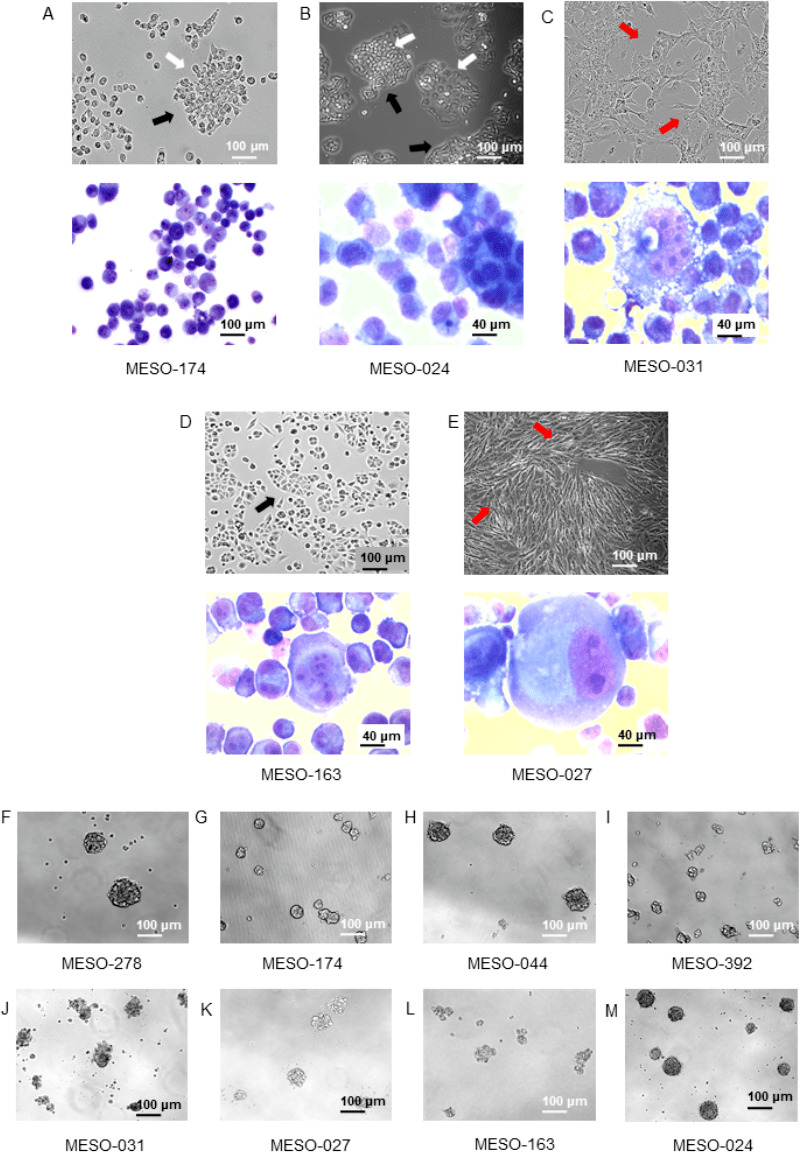
Patient-derived malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) cell cultures originated from malignant pleural effusion specimens are truly cancerous and showed tumour stemness properties. (A–E) Top: phase contrast images (10× magnification) of representative MPM cells in culture showing colony formation (white arrows), cobblestone (black arrows) and spindle (red arrows) shapes. Bottom: May Grunwald Giemsa-stained cytospin specimens of selected MPM cell cultures showing (A) pleomorphic and multiple nucleoli (10× magnification), (B) small atypical nucleoli and two-tone cytoplasm typical of mesothelial morphology (40× magnification), (C) atypical features with large nucleus and very large nucleoli (40× magnification), (D) bizarre nucleus with multiple nucleoli (40× magnification), (E) large and multiple nuclei (binucleate) and atypical and multiple nucleoli (40× magnification). (F–M) Phase contrast images of tumour-spheroids formed by MPM patient-derived cancer cell cultures (10× magnification). Patient-derived MPM cell cultures were able to form tumour-spheres highlighting tumour stemness properties and the existence of a cancer stem cell subpopulation.
