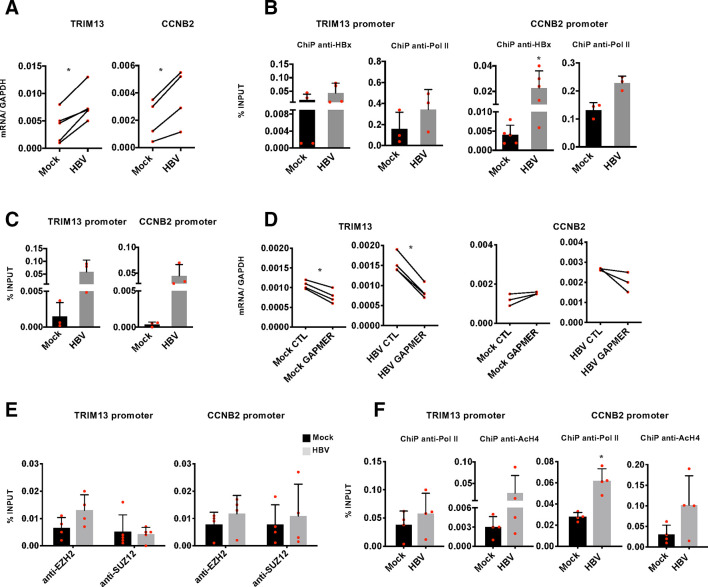
Figure 6.
DLEU2 and HBx cooperate to activate TRIM13 and CCNB2 transcription. (A) Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) of TRIM13 and CCNB2 mRNA in mock-infected and HBV-infected primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) (7 days). Results are expressed as relative values to endogenous human GAPDH mRNAs. (B) HBx occupancy and modulation of polymerase II (Pol II) binding on TRIM13 and CCNB2 promoters in mock-infected and HBV-infected PHHs (72 hours) by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. The detection of HBV covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) using specific primers in the ChIPed DNA from HBV-infected cells (cccDNA-ChIP) served as a technical positive control for the ChIP procedure. ChIP results are expressed as % of input. (C) DLEU2-ChIRP for TRIM13 promoter or CCNB2 promoter using DLEU2-specific antisense DNA probe in mock-replicating and HBV-replicating HepG2 cells (48 hours). (D) Real-time qPCR of TRIM13 and CCNB2 cDNA in mock-infected or HBV-infected PHHs transfected (4 days) with scrambled Gapmer (CTL) or with DLEU2 Gapmer (GAPMER). Results are expressed as relative values to endogenous human GAPDH mRNAs. (E) Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and SUZ12 occupancy on TRIM13 and CCNB2 promoter regions by ChIP assay in mock-infected and HBV-infected HepG2-NTCP cells (7 days). Anti-CTCF ChIPs were included as a technical positive control. Results are expressed as % of input. (F) Modulation of H4 acetylation and Pol II binding on the TRIM13 and CCNB2 promoters in HBV-infected HepG2-NTCP cells (7 days). Results are expressed as % of input. Data in panels (A) to (F) represent means±SD from at least three independent experiments. In (A), (B), (D) and (F), *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test.