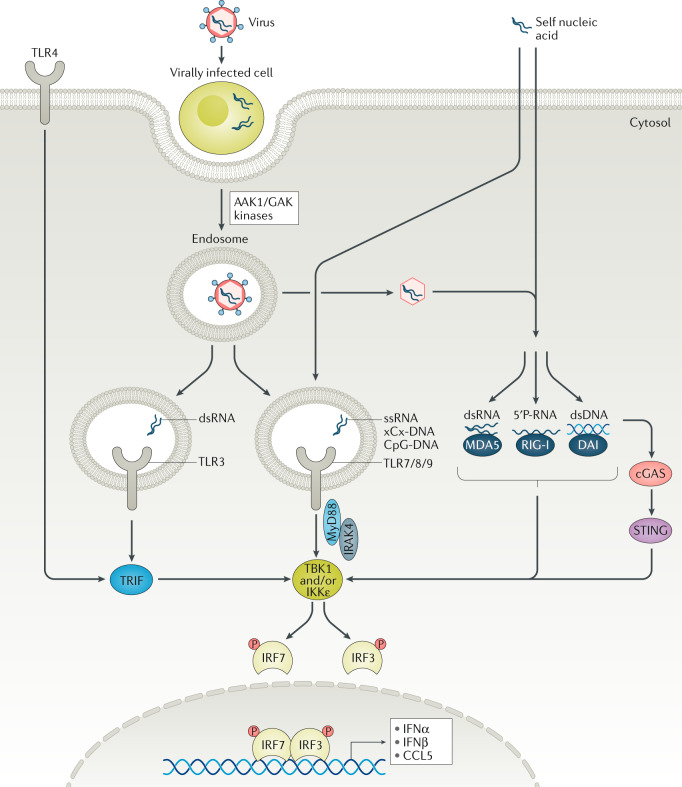
Fig. 7. IKKε and TBK1 kinases integrate signalling from nucleic acid sensors.
Nucleic acid sensors include the endosomal Toll-like receptors (TLRs) TLR3, TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9; the cytosolic DNA sensor cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS); and retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs). RLRs are RNA sensors that include RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5). Unusual RNAs (double-strand RNA (dsRNA), 5′-phosphorylated (5′P) mRNA) can activate RIG-I or MDA5. Multimerized RIG-I and MDA5 can then bind to create a mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein (MAVS), mitochondrial-associated membranes and peroxisomes, which in turn activate TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and inhibitor of NF-κB subunit-ε (IKKε) to activate interferon-regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and IRF7. Double-stranded DNA (dsDNA; such as self-DNA) can induce an allosteric structural change in cGAS that, in turn, activates second messengers to promote stimulator of interferon genes (STING) to undergo dimerization to form a complex with TBK1 and IKKε that phosphorylates IRF3 to activate gene transcription. DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI; also known as Z-DNA-binding protein 1 (ZBP1)) can also act as a sensor of Z-dsDNA (left-handed double-helical structure), often acquired during viral infection in a cell type-specific manner. DAI recruits TBK1 and IRF3 upon DNA binding and may get further phosphorylated to amplify the DAI/TBK1/IRF3 circuit265. Numb-associated kinases (adaptor protein 2 (AP2)-associated protein kinase 1 (AAK1) and cyclin G-associated kinase (GAK)) regulate intracellular viral trafficking during entry, assembly and release of unrelated viruses. Disruption of endocytosis by inhibiting AAK1/GAK can prevent the virus passage into cells. Endosomal TLRs (TLR7/8/9) recruit myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) and signal through IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) to activate IRFs similar to cell surface TLRs (see Fig. 3). TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing IFNβ (TRIF)-dependent and MyD88-independent signalling could also activate TBK1/IKKε to activate IRF-mediated gene transcription. P, phosphorus; ssDNA, single-strand DNA.