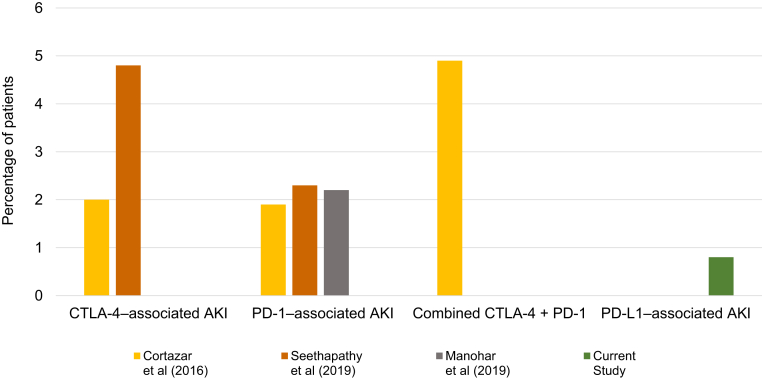
Figure 3.
Incidence of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1)–related acute kidney injury (AKI) compared to historical estimates of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte−associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell death 1 receptor (PD-1), and CTLA-4/PD-1 combination therapy–related AKI. The incidence of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)–related AKI from clinical trial data was gathered in 2 meta-analyses (Cortazar et al.2 [2016] and Manohar et al.5 [2019]) and 1 observational real-world study (Seethapathy et al.4 [2019]). The incidence of CTLA-4–related AKI was 2% in Cortazar et al. and 4.8% in Seethapathy et al. The incidence of PD-1 related AKI was 1.9% in Cortazar et al., 2.2% in Manohar et al., and 2.3% in Seethapathy et al. The incidence of ICI-AKI with combination CTLA-4 and PD-1 therapy was 4.9% from Cortazar et al. In comparison, the incidence of PD-L1–related AKI was 0.8% in our study.