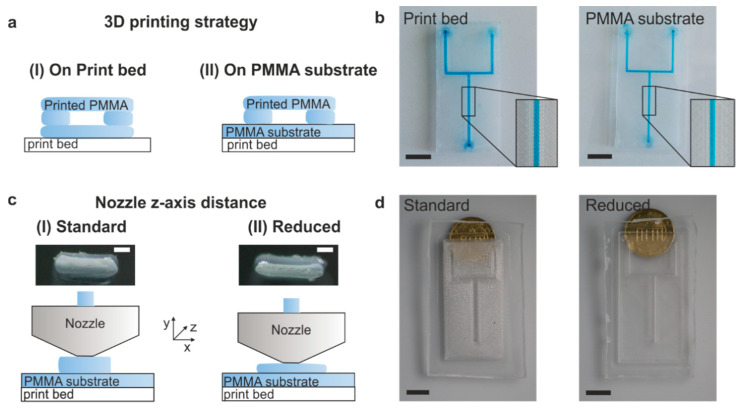
Figure 1.
Fused deposition modeling of microfluidic chips in polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). (a) Principle of printing microfluidic PMMA channels. PMMA was either directly printed on the print bed (I) or printed on top of a commercial PMMA slide (II). (b) Comparison of two identical microfluidic chips directly printed on the print bed and printed on a commercial PMMA substrate, respectively. As can be seen, the transparency in the region of interest is increased by printing on a commercial PMMA substrate (scale bars: 10 mm). (c) Increasing the optical transparency by reducing the nozzle distance: (I) standard configuration, (II) printing with a reduced nozzle distance which flattens the extruded filament. The nozzle is moving in the z-direction. The images show the 3D printed cross-section of the first layer calibration (scale bar: 100 µm). (d) Comparison of microfluidic channels printed with standard configuration and with reduced nozzle distance. As can be seen the transparency is increased for the printing setup with reduced nozzle distance (scale bar: 10 mm).