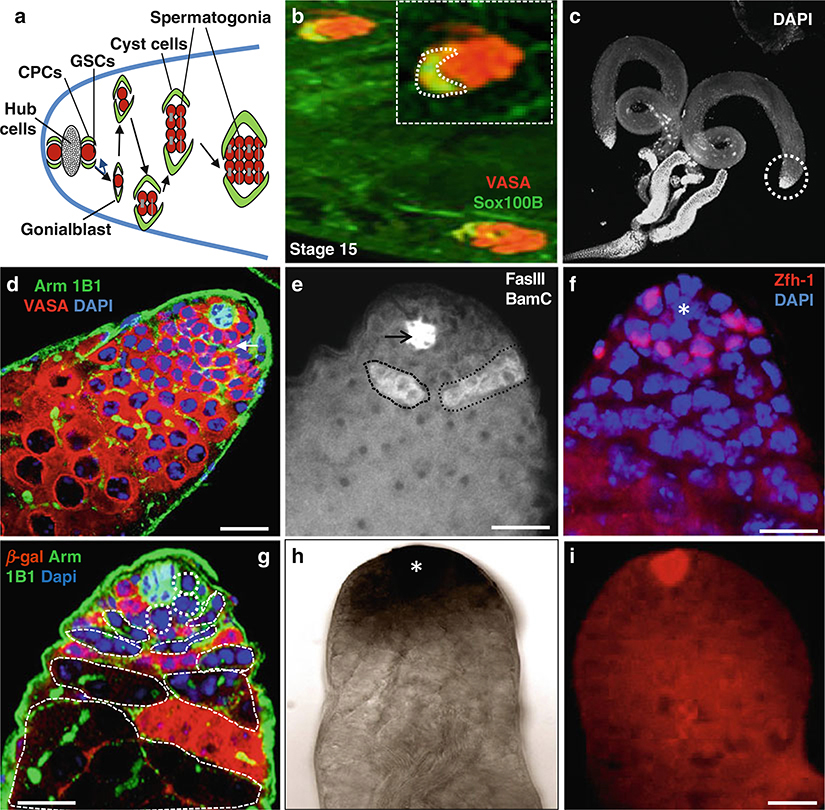
Fig. 1.
Immunostaining and in situ hybridization of Drosophila testes. (a) Schematic diagram highlights the tip of the testes, which usually contain five to nine GSCs; only two GSCs are shown in this diagram, surrounded by about twice as many cyst progenitor cells (CPCs). Both GSCs and CPCs anchor around the hub cells, which act as niche cells. The testis proliferation center consists of hub, GSCs, CPCs, gonialblasts, and 2- to 16-cell spermatogonia. (b) Wild-type stage 15 embryonic testes stained with anti-Vasa (red ) to mark the germline and anti-Sox100B (green) representing the male- specific somatic gonadal precursor (msSGP) cells. (c) Wild-type testes stained with DAPI. (d) Wild-type testis stained with anti-Arm (green) to mark the hub cells, 1B1 to mark the spectrosomes and fusome (green), and anti-Vasa (red) marks all germ cells including GSCs. (e) Wild-type testis stained with anti-BamC to mark the spematogonial cells (white color positive cells inside black dotted lines) and anti-FasII to mark hub cells (black arrow). (f) Wild-type testis stain with anti-Zfh-1 (red) to mark cyst stem cells. (g) Wild type 6 days after heat shock GSC clones highlighted by dotted lines. Testis stained with anti-β-galactosidase (red), anti-Arm and anti1b1 (green). (h) Wild-type testis with Gef26 mRNA expression. (j) Wild-type testis with upd mRNA expression (red) using Fast red FISH. Dapi marks DNA (blue) in (d, f, g). Scale bars: 20 μm (b); 10 μm (d-G, I)